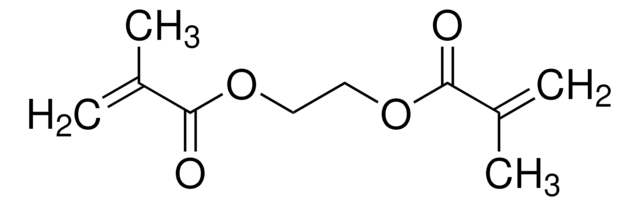
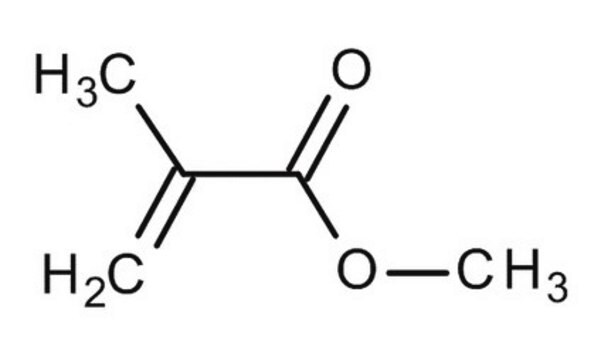
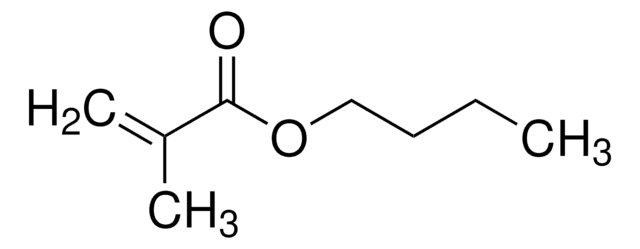
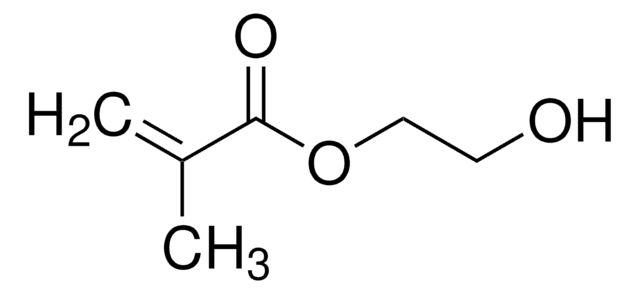
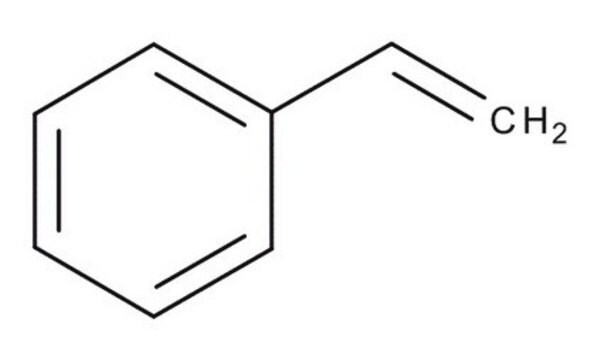
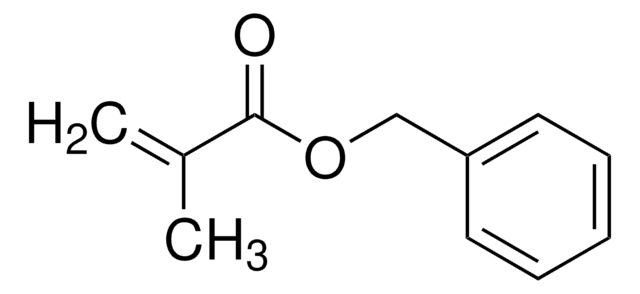
おすすめの製品
蒸気密度
3.5 (vs air)
品質水準
蒸気圧
29 mmHg ( 20 °C)
アッセイ
99%
自己発火温度
815 °F
含みます
≤30 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
expl. lim.
12.5 %
屈折率
n20/D 1.414 (lit.)
bp
100 °C (lit.)
mp
−48 °C (lit.)
密度
0.936 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
保管温度
2-8°C
SMILES記法
COC(=O)C(C)=C
InChI
1S/C5H8O2/c1-4(2)5(6)7-3/h1H2,2-3H3
InChI Key
VVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
類似した製品をお探しですか? 訪問 製品比較ガイド
詳細
アプリケーション
- ランタニド錯体でグラフト化したポリ(メタクリル酸メチル-無水マレイン酸)コポリマー。これらの発光ポリマーは高い熱安定性を示し、光電子デバイスの発光層として使用できます。
- ポリ(メタクリル酸メチル)(PMMA)。これは集光型太陽光発電(CPV)モジュール用のレンズの製造に使用される一般的な材料です。
- ポリメタクリル酸メチル、メタクリル酸メチルクロスポリマー、メタクリル酸メチル/ジメタクリル酸グリコールクロスポリマー。これらのポリマーは、美容外科、歯科、関節置換術で使用されています。
- ポリ(メタクリル酸メチル)(PMMA)ベースの個別化医療機器。
- 熱的および機械的特性が強化された、相互浸透したメタクリル酸メチルベースのポリマーネットワーク。
- 乳化共重合によるポリ(メタクリル酸メチル-メタクリル酸ヒドロキシエチル)(PMMA-co-PHEMA)コポリマー。これらのコポリマーは、熱酸化的に安定で、引き延ばせるフィルムを形成します。
- ディファレンシャル・マイクロエマルション重合によるポリ(メタクリル酸メチル)ナノ粒子。
シグナルワード
Danger
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1B - STOT SE 3
ターゲットの組織
Respiratory system
保管分類コード
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 1
引火点(°F)
50.0 °F - closed cup
引火点(℃)
10 °C - closed cup
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
PRTR
第一種指定化学物質
消防法
第4類:引火性液体
第一石油類
危険等級II
非水溶性液体
労働安全衛生法名称等を表示すべき危険物及び有害物
名称等を表示すべき危険物及び有害物
労働安全衛生法名称等を通知すべき危険物及び有害物
名称等を通知すべき危険物及び有害物
Jan Code
M55909-VAR:
M55909-25KG:
M55909-17L:4548173950235
M55909-1L:4548173950242
M55909-2L:4548173950266
M55909-10L:
M55909-25ML:4548173950259
M55909-2.5L:
M55909-25L:
M55909-500ML:4548173950273
M55909-BULK:
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
資料
RAFT (Reversible Addition Fragmentation chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
RAFT (Reversible Addition Fragmentation chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
The manufacture of monomers for use in ophthalmic applications is driven by the need for higher purity, improved reliability of manufacturing supply, but ultimately by the need for the increased comfort, convenience, and safety of contact lens wearers. Daily wear contact lenses have the potential to fill this need for many customers; however, their widespread use is constrained by higher costs compared to weekly- or monthly-based lenses. New approaches that improve cost structure and result in higher quality raw materials are needed to help make contact lenses more affordable and accelerate growth of the contact lens market.
The manufacture of monomers for use in ophthalmic applications is driven by the need for higher purity, improved reliability of manufacturing supply, but ultimately by the need for the increased comfort, convenience, and safety of contact lens wearers. Daily wear contact lenses have the potential to fill this need for many customers; however, their widespread use is constrained by higher costs compared to weekly- or monthly-based lenses. New approaches that improve cost structure and result in higher quality raw materials are needed to help make contact lenses more affordable and accelerate growth of the contact lens market.
プロトコル
Monodisperse, surfactant-free polymer spheres for use as colloidal crystal templates can be easily obtained in reasonably large quantities. Typical synthesis methods for poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) and poly(styrene) (PS) by emulsifier free emulsion polymerization are described below and yield spheres several hundred nanometers in diameter.
RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation chain Transfer) is a form of living radical polymerization involving conventional free radical polymerization of a substituted monomer in the presence of a suitable chain transfer (RAFT) reagent.
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)