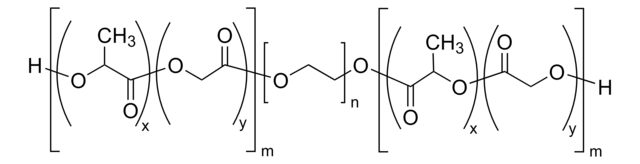
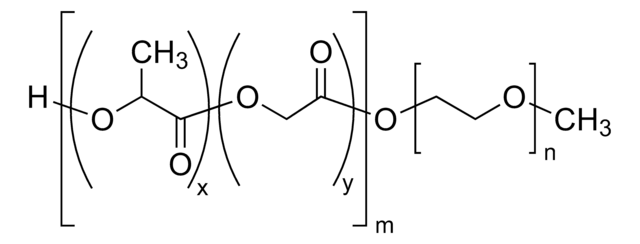
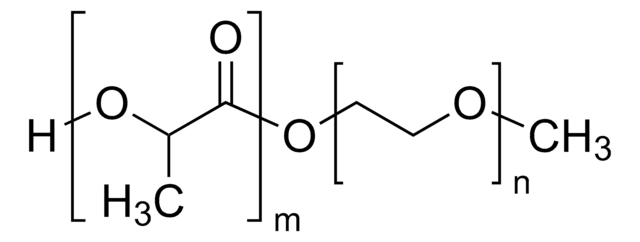
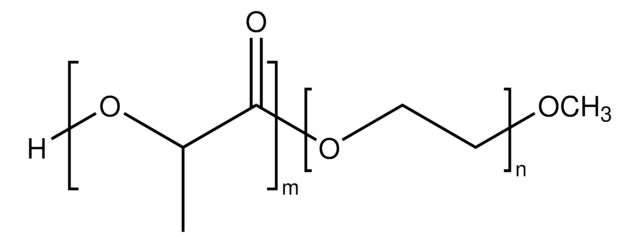
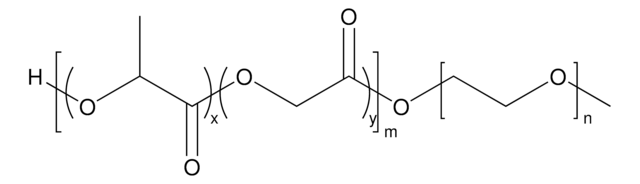
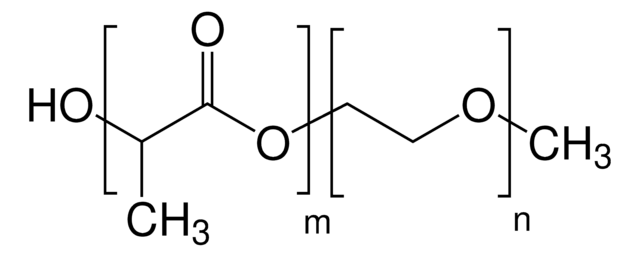
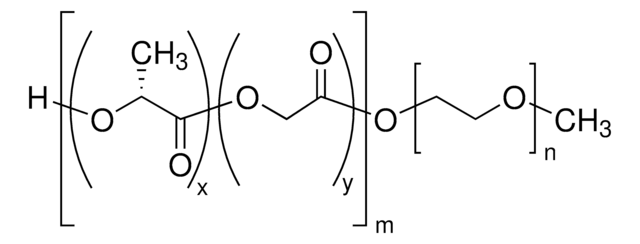
おすすめの製品
詳細
アプリケーション
特徴および利点
- 良好な生体適合性、低い免疫原性、および良好な分解性
- 特定の用途に合わせてブロックコポリマーセグメントのサイズを変更することにより、特性を簡単に調節できます。
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
No data available
引火点(℃)
No data available
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
765139-1G:
765139-BULK:
765139-VAR:
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
資料
One of the common difficulties with intravenous drug delivery is low solubility of the drug. The requirement for large quantities of saline to dissolve such materials limits their clinical use, and one solution for this problem that has recently generated interest is the formation of drug-loaded micelles.
One of the common difficulties with intravenous drug delivery is low solubility of the drug. The requirement for large quantities of saline to dissolve such materials limits their clinical use, and one solution for this problem that has recently generated interest is the formation of drug-loaded micelles.
Local delivery of bioactive molecules using an implantable device can decrease the amount of drug dose required as well as non-target site toxicities compared to oral or systemic drug administration.
Local delivery of bioactive molecules using an implantable device can decrease the amount of drug dose required as well as non-target site toxicities compared to oral or systemic drug administration.
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)