M7504
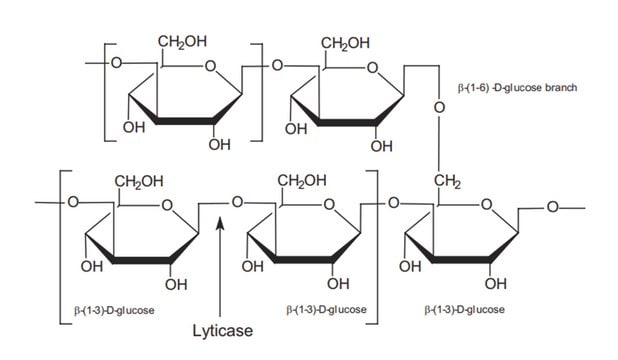
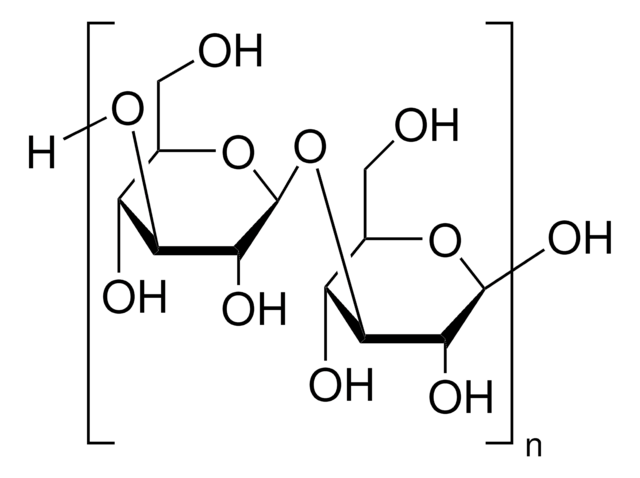
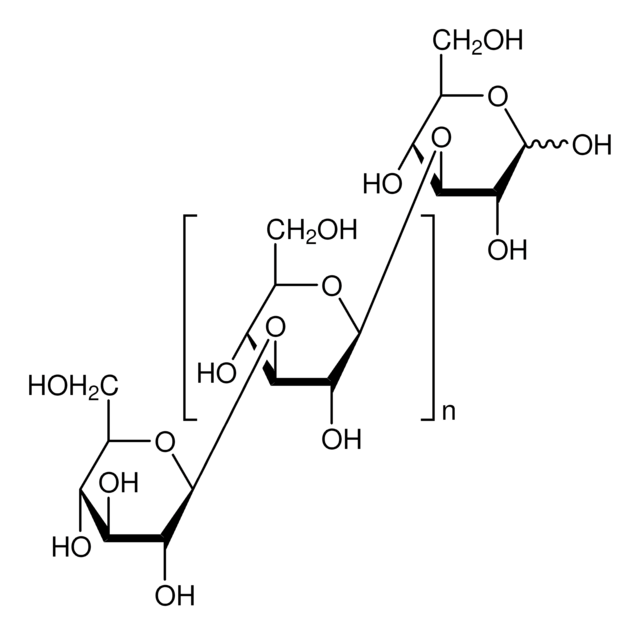
Mannan from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
prepared by alkaline extraction
Synonym(s):
D-Mannan
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bakers yeast (whole cell)
Quality Level
form
powder
optical activity
[α]/D 73 to 89 °, c = 1% (w/v) in water
impurities
<1.0% Low molecular weight saccharides (TLC)
color
beige
solubility
water: ~50 g/L
cation traces
Na: <2%
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Preparation Note
Other Notes
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
M7504-5G:
M7504-100MG:
M7504-VAR:
M7504-250MG:
M7504-BULK:
M7504-1G:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service