L6638
Lipid A, monophosphoryl from Escherichia coli F583 (Rd mutant)
lyophilized powder
Sinonimo/i:
E. coli Monophosphoryl Lipid A
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
Escherichia coli (F583 Rd mutant)
Livello qualitativo
Stato
lyophilized powder
Impurezze
<0.2% Ketodeoxyoctonate (KDO)
Condizioni di spedizione
ambient
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Azioni biochim/fisiol
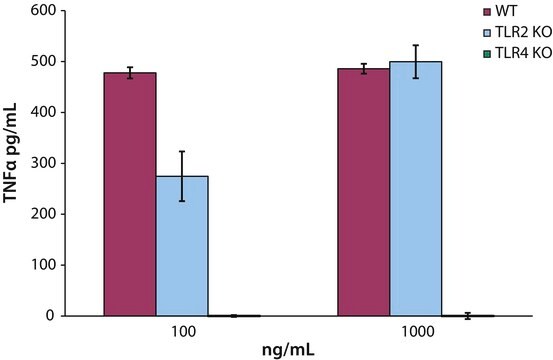
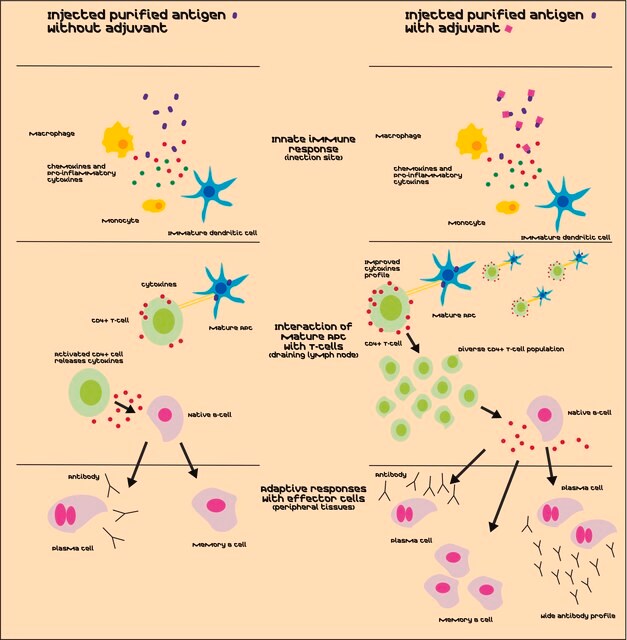
Lipid A has immunostimulatory adjuvant activity including macrophage, T-cell, and B-cell activation. Research has shown Lipid A has greater Th1 than Th2 stimulation.
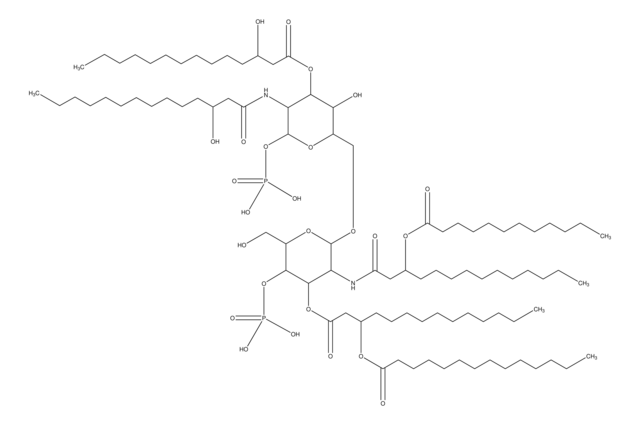
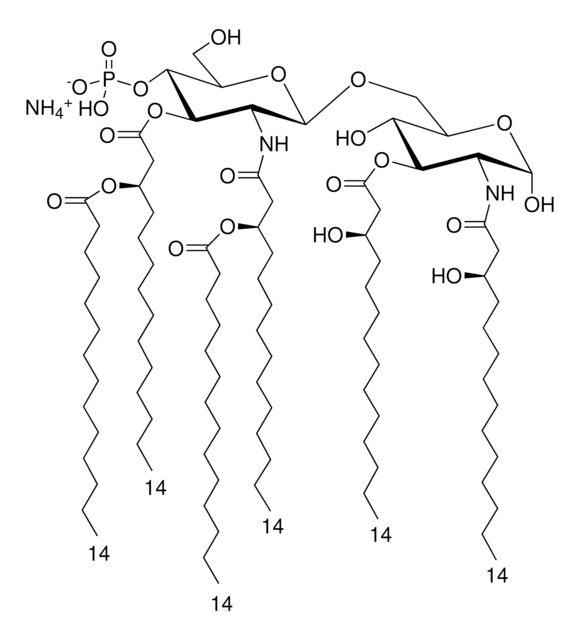
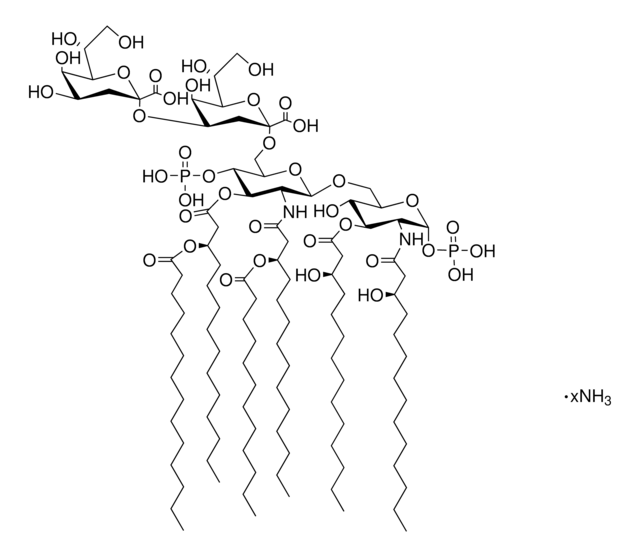
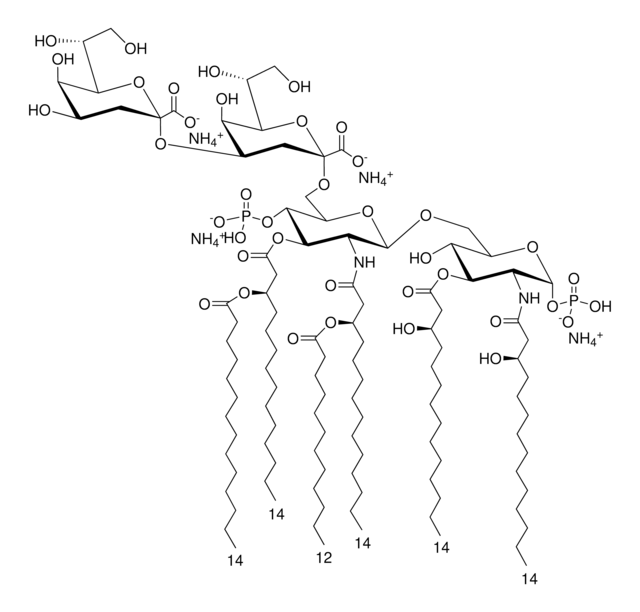
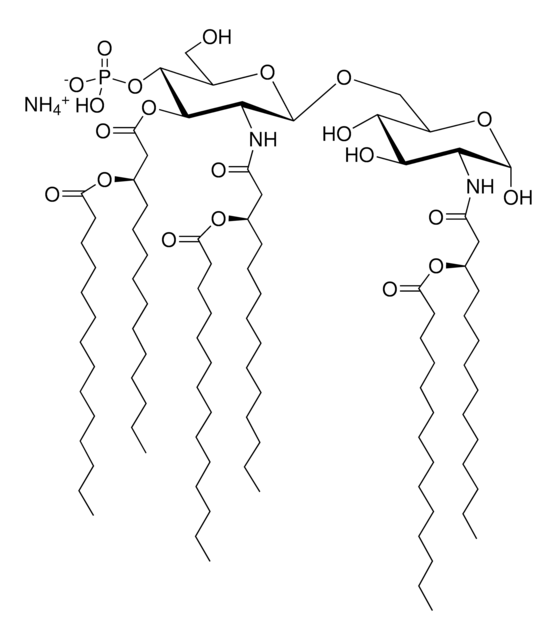
Lipid A molecules compose the lipid membrane anchoring core components of endotoxins produced by Gram-negative bacteria. Lipid A molecules induce immune responses. Structually, lipid A molecules are composed of two glucosamine unites with varied, species dependent, fatty acyl chain number and identity and degree of phosphorylation.
Lipid A, monophosphoryl from Escherichia coli F583 may be used in comparative assessment of the antigenicity of specific structures within different LPA molecules and analogues.
Lipid A, monophosphoryl from Escherichia coli F583 may be used in comparative assessment of the antigenicity of specific structures within different LPA molecules and analogues.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Vincent J Venditto et al.
Clinical and vaccine immunology : CVI, 21(8), 1086-1093 (2014-05-30)
Broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (bNAbs) 2F5 and 4E10 bind to the membrane proximal external region (MPER) of gp41 and also cross-react with phospholipids. In this study, we investigated if chemical modifications on the MPER adjacent to 2F5 and 4E10 epitopes
Vincent J Venditto et al.
Clinical and vaccine immunology : CVI, 20(1), 39-45 (2012-11-02)
The inability to generate broadly neutralizing antibody (bnAb) responses to the membrane proximal external region (MPER) of HIV-1 gp41 using current vaccine strategies has hampered efforts to prevent the spread of HIV. To address this challenge, we investigated a novel
Mark B Stoddard et al.
Clinical and vaccine immunology : CVI, 17(1), 98-107 (2009-11-20)
Bacterial endotoxin interacts with the human immune system via complex immunological pathways. The evaluation of endotoxicity is important in the development of safe vaccines and immunomodulatory therapeutics. The Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) assay is generally accepted by the FDA for
Douglas S Watson et al.
Clinical and vaccine immunology : CVI, 18(2), 289-297 (2010-12-17)
Particulate delivery systems enhance antibody responses to subunit antigens. However, covalent attachment of protein antigens can disrupt protein structure and mask critical epitopes, altering the antibody response to the antigen. In this report, we evaluate noncovalent metal chelation via nitrilotriacetic
Hong Zhao et al.
PLoS pathogens, 10(4), e1004009-e1004009 (2014-04-12)
Metarhizium robertsii is a plant root colonizing fungus that is also an insect pathogen. Its entomopathogenicity is a characteristic that was acquired during evolution from a plant endophyte ancestor. This transition provides a novel perspective on how new functional mechanisms
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.