A5512
Aristolochic acid I
≥90% (HPLC), powder, phospholipase A₂ inhibitor
Sinonimo/i:
TR 1736
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
product name
Aristolochic acid I, powder
Saggio
≥90% (HPLC)
Forma fisica
powder
Colore
yellow
Punto di fusione
269-270 °C
Solubilità
DMSO: soluble
ethanol: soluble
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
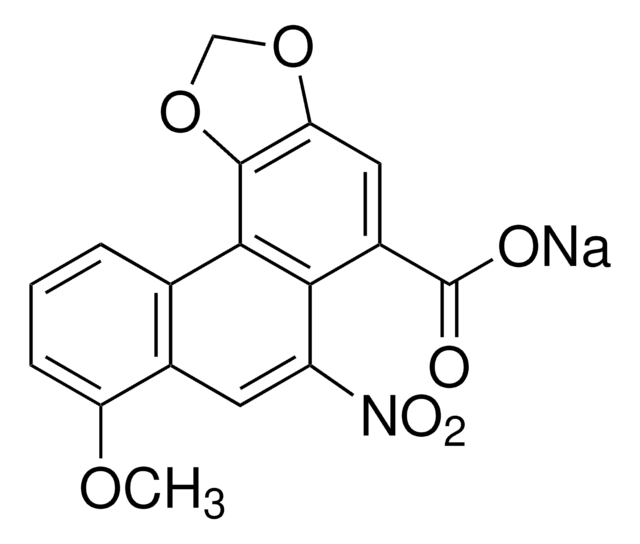
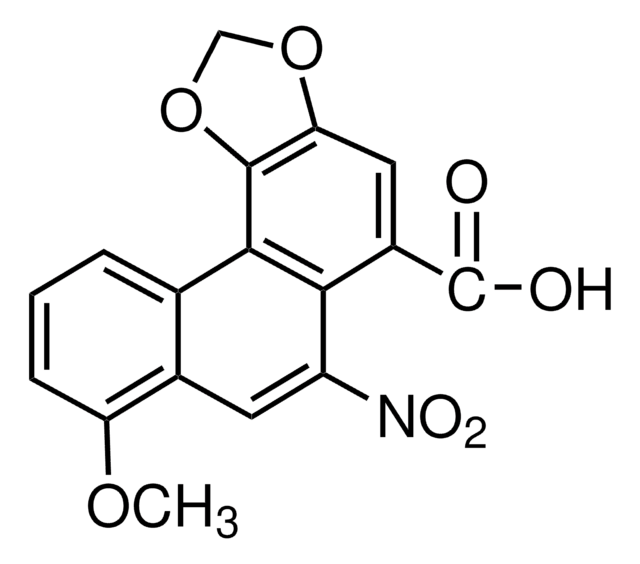
Stringa SMILE
COc1cccc2c1cc([N+]([O-])=O)c3c(cc4OCOc4c23)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C17H11NO7/c1-23-12-4-2-3-8-9(12)5-11(18(21)22)14-10(17(19)20)6-13-16(15(8)14)25-7-24-13/h2-6H,7H2,1H3,(H,19,20)
BBFQZRXNYIEMAW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- as a standard for the analysis of Aristolochia sprucei crude extract by high-performance liquid chromatography
- to study its effects on histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) aberration and renal fibrosis
- to induce acute aristolochic acid nephropathy and to study its impact on miRNA and mRNA expression in mice
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Carc. 1A - Muta. 1B
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
Carcinogenesis and Epigenetics
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.