11699105001
Roche
PCR Buffer Without MgCl2, 10x concentrated
solution, pkg of 3 × 1 mL
Sinonimo/i:
buffer
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Codice UNSPSC:
41105600
Prodotti consigliati
Stato
solution
Livello qualitativo
Confezionamento
pkg of 3 × 1 mL
Produttore/marchio commerciale
Roche
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
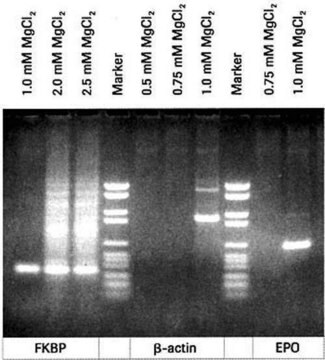
The PCR buffer without MgCl2, in combination with the MgCl2 stock solution, is used for the individual adjustment of the Mg2+ concentration in the PCR reaction. In most applications a concentration of 1.5mM MgCl2 will yield satisfactory results with a dNTP concentration of 200μM each. In many cases, however, it is required to titrate the optimal Mg2+ concentration to increase the specificity and yield of the PCR reaction.The buffer is ten-fold concentrated and should be used in combination with the MgCl2 stock solution.
Applicazioni
The PCR buffer without MgCl2 has been used for the amplification of specific DNA fragments by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Stato fisico
Solution, 100 mM Tris-HCl, 500 mM KCl (pH 8.3 at 20 °C)
Altre note
For general laboratory use.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
does not flash
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
does not flash
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Rao L Divi et al.
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology, 118(1), 191-201 (2010-08-13)
Mitochondrial compromise has been documented in infants born to women infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) who received nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) therapy during pregnancy. To model these human exposures, we examined mitochondrial integrity at birth and 1
Omid Yeganeh et al.
Iranian Red Crescent medical journal, 15(4), 340-344 (2013-10-02)
Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma genitalium infections are the most prevalent sexually transmitted bacterial infections in the world that cause urogenital infections in both men and women. It appears that infertility is a complication of these infections. This study was designed
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.