W265501
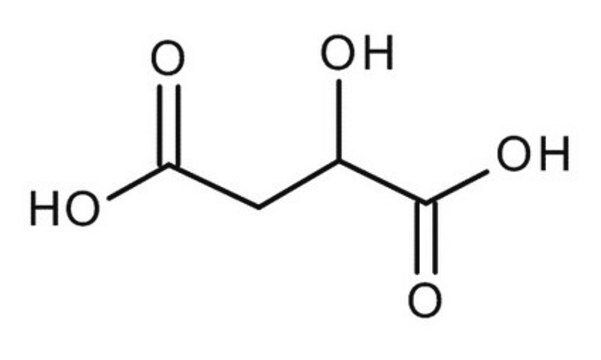
DL-Malic acid
99%
Sinonimo/i:
(±)-2-Hydroxysuccinic acid, DL-Hydroxybutanedioic acid
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
synthetic
Livello qualitativo
Grado
Kosher
Conformità normativa
FDA 21 CFR 1084.1069
FDA 21 CFR 117
Densità del vapore
4.6 (vs air)
Tensione di vapore
<0.1 mmHg ( 20 °C)
Saggio
99%
Temp. autoaccensione
644 °F
Punto di fusione
131-133 °C (lit.)
Solubilità
H2O: soluble 646.6 g/L at 20 °C
applicazioni
flavors and fragrances
Documentazione
see Safety & Documentation for available documents
Allergene alimentare
no known allergens
Organolettico
odorless
Stringa SMILE
OC(CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H6O5/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2,5H,1H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)
BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- Tetra-Ln(3+)-Implanted Tellurotungstates Covalently Modified by dl-Malic Acid: Proton Conduction and Photochromic Properties.: This innovative study showcases dl-Malic acid as a key component in the synthesis of advanced tellurotungstates, contributing to notable enhancements in proton conduction and photochromic properties, which are critical for applications in smart materials and sensors (Niu et al., 2024).
- Direct regeneration of spent LiFePO(4) materials via a green and economical one-step hydrothermal process.: dl-Malic acid is utilized in a green chemistry approach for the direct regeneration of lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) materials, demonstrating a sustainable pathway for battery recycling and highlighting its importance in promoting environmental sustainability (Yang et al., 2023).
- Chitin Extracted from the Shell of Blue Swimming Crabs (Portunus pelagicus Linn.) Inhibits NF-kappaB p65 in Ethanol-Induced Gastric Ulcerative Wistar Rats.: In this research, dl-Malic acid serves as a catalyst in the extraction and functional activity testing of chitin, which is shown to have significant anti-inflammatory effects, suggesting its potential in pharmaceutical applications (Amelia et al., 2023).
- Manganese-Titanium Mixed Ion Sieves for the Selective Adsorption of Lithium Ions from an Artificial Salt Lake Brine.: Highlighting the application of dl-Malic acid in the synthesis of ion-exchange materials, this study points towards its utility in enhancing the selective adsorption properties of manganese-titanium mixed ion sieves, crucial for lithium recovery from brines (Ding et al., 2023).
Esclusione di responsabilità
Avvertenze
Warning
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Eye Irrit. 2
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
397.4 °F
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
203 °C
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.