529265
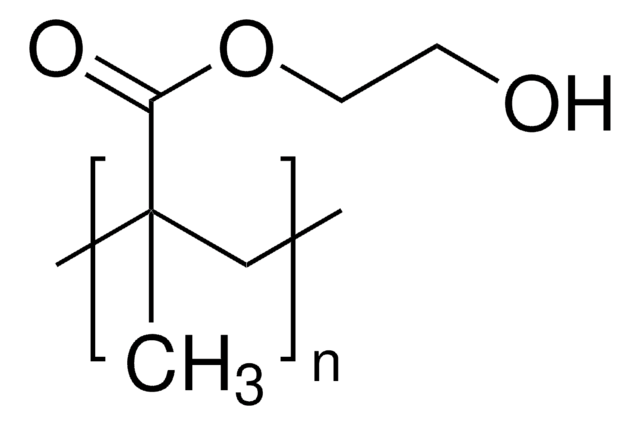
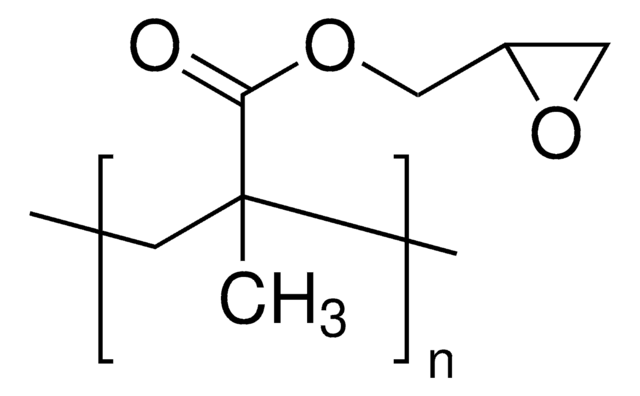
Poli(2-idrossietil metacrilato)
average Mv 20,000
Sinonimo/i:
Poli(2-HEMA), Poli-HEMA
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Stato
powder
Livello qualitativo
PM
average Mv 20,000
Temp. transizione
Tg 84.8 °C
Densità
1.15 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Stringa SMILE
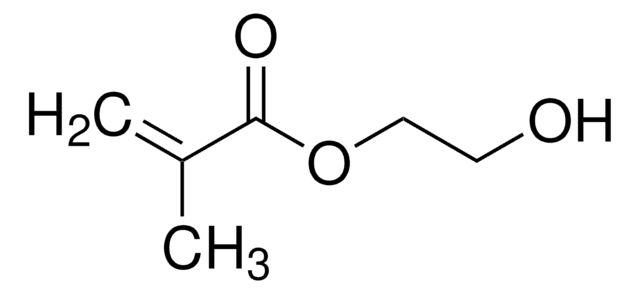
CC(=C)C(=O)OCCO
InChI
1S/C6H10O3/c1-5(2)6(8)9-4-3-7/h7H,1,3-4H2,2H3
WOBHKFSMXKNTIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Categorie correlate
Applicazioni
- Hydrogen-bonds structure in poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) studied by temperature-dependent infrared spectroscopy: Investigates the hydrogen-bond structure in poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PHEMA) using temperature-dependent IR spectroscopy. (S Morita, 2014).
- Transparent and tough poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogels prepared in water/IL mixtures: Describes the development of tough and transparent PHEMA hydrogels for potential use in various biomedical applications. (Y Liu et al., 2020).
- Reduced cell attachment to poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)-coated ventricular catheters in vitro: Examines how PHEMA coatings can reduce cell attachment, which is beneficial for biomedical devices like catheters. (BW Hanak et al., 2018).
- Surface modification of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogel for contact lens application: Studies modifications to PHEMA hydrogels to improve their suitability for contact lens applications. (M Kazemi Ashtiani, M Zandi, 2018).
Stato fisico
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
Professor Shrike Zhang (Harvard Medical School, USA) discusses advances in 3D-bioprinted tissue models for in vitro drug testing, reviews bioink selections, and provides application examples of 3D bioprinting in tissue model biofabrication.
Professor Shrike Zhang (Harvard Medical School, USA) discusses advances in 3D-bioprinted tissue models for in vitro drug testing, reviews bioink selections, and provides application examples of 3D bioprinting in tissue model biofabrication.
Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) have attracted enormous interest for a wide variety of applications in micro- and nano-technology. In this article, we compare the benefits of three different classes of SAM systems (alkylthiolates on gold.
Biomaterials science involves the design and fabrication of smart materials for studying, directing, or mimicking biology. For successful integration of biomaterials in biological research, a meaningful understanding of biological systems is required.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 529265-25G | 4061833598955 |
| 529265-5G | 4061832558028 |
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.