201146
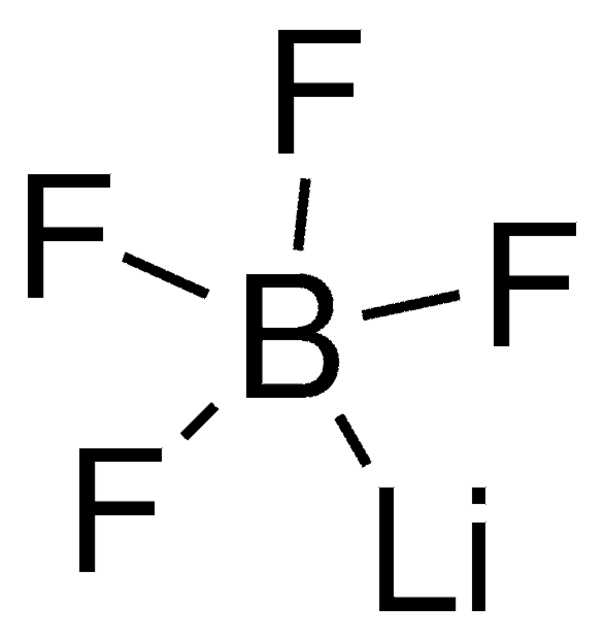
Lithium hexafluorophosphate
98%
Sinonimo/i:
Lithium phosphorus fluoride
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Grado
for analytical purposes
Saggio
98%
Stato
powder
Punto di fusione
200 °C (dec.) (lit.)
Solubilità
H2O: slightly soluble(lit.)
Densità
1.5 g/mL (lit.)
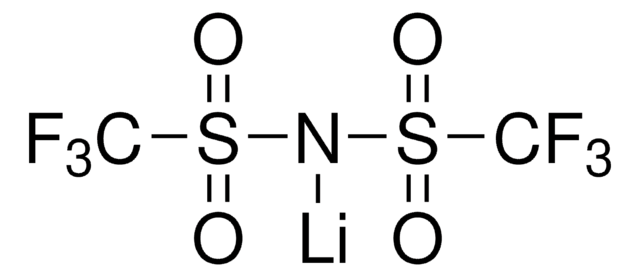
Stringa SMILE
[Li+].F[P-](F)(F)(F)(F)F
InChI
1S/F6P.Li/c1-7(2,3,4,5)6;/q-1;+1
AXPLOJNSKRXQPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
- It can form suitable SEI membranes in electrodes, especially in the cathode
- It can implement passivation for anode current collectors to prevent their dissolution
- Wide windows of electrical stability
- Excellent solubility and high conductivity in various solvents
- Environment-friendly
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1A - STOT RE 1 Inhalation
Organi bersaglio
Bone,Teeth
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 2
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
Research and development of solid-state lithium fast-ion conductors is crucial because they can be potentially used as solid electrolytes in all-solid-state batteries, which may solve the safety and energy-density related issues of conventional lithium-ion batteries that use liquid (farmable organic) electrolytes.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.