163201
N,N′-Dicyclohexyl-4-morpholinecarboxamidine
98%
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Formula empirica (notazione di Hill):
C17H31N3O
Numero CAS:
Peso molecolare:
293.45
Numero CE:
Numero MDL:
Codice UNSPSC:
12352100
ID PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.22
Prodotti consigliati
Saggio
98%
Punto di fusione
105-107 °C (lit.)
Gruppo funzionale
amine
Stringa SMILE
C1CCC(CC1)N\C(=N\C2CCCCC2)N3CCOCC3
InChI
1S/C17H31N3O/c1-3-7-15(8-4-1)18-17(20-11-13-21-14-12-20)19-16-9-5-2-6-10-16/h15-16H,1-14H2,(H,18,19)
OZNYZQOTXQSUJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
N,N′-Dicyclohexyl-4-morpholinecarboxamidine is kidney-selective ATP-sensitive potassium blocker. It is an an orally effective nonkaliuretic diuretic in rats.
Applicazioni
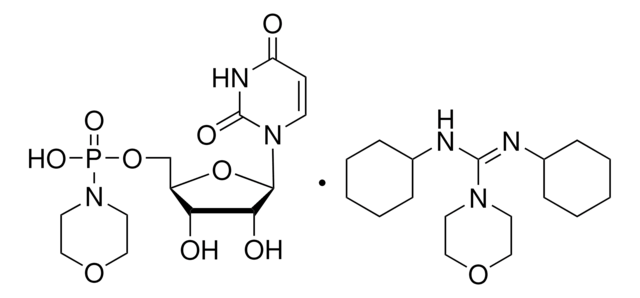
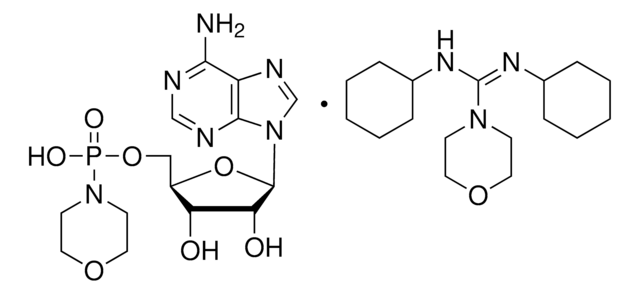
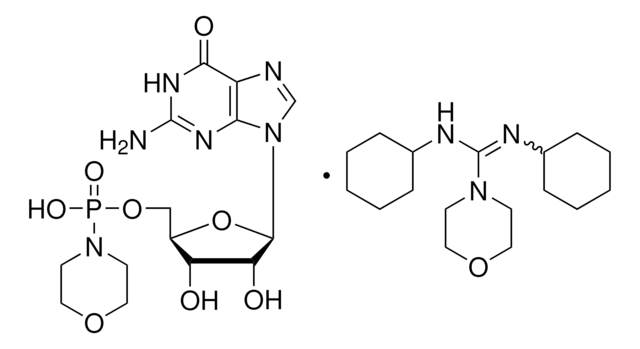
N,N′-Dicyclohexyl-4-morpholinecarboxamidine was used as reagent in the synthesis of alkoxyalkyl analogs of nucleotide phosphonates, cidofovir and cyclic cidofovir.
Avvertenze
Warning
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organi bersaglio
Respiratory system
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
S C Perricone et al.
Journal of medicinal chemistry, 37(22), 3693-3700 (1994-10-28)
Random screening identified N,N'-dicyclohexyl-4-morpholinecarboxamidine (U-18177, 1) as an orally effective nonkaliuretic diuretic in rats. The diuretic profile of 1 and its 1-adamantyl analog (U-37883A, 4) was confirmed orally in dogs, when they were less potent than standard diuretics but showed
Earl R Kern et al.
Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 46(4), 991-995 (2002-03-19)
The nucleotide phosphonates cidofovir (CDV) and cyclic cidofovir (cCDV) are potent antiviral compounds when administered parenterally but are not well absorbed orally. These compounds have been reported to have activity against orthopoxvirus replication in vitro and in animal models when
Yuji Kamata et al.
Hypertension research : official journal of the Japanese Society of Hypertension, 32(3), 220-226 (2009-03-06)
It is suggested that an ATP-sensitive potassium channel blocker suppresses sodium-induced hypertension through increased secretion of urinary kallikrein. We reported that glibenclamide, an ATP-sensitive potassium channel blocker, accelerated dose-dependent secretion of renal kallikrein in sliced kidney cortex and in vivo
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.