推荐产品
生物源
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
human herpesvirus 2
重組細胞
expressed in E. coli
化驗
≥80% (SDS-PAGE)
形狀
frozen liquid
分子量
~27.8 kDa
包裝
pkg of 10 and 500 μg
儲存條件
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
濃度
500 μg/mL
技術
electrophoretic mobility shift assay: suitable
顏色
colorless to clear
NCBI登錄號
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−70°C
基因資訊
Saccharomyces cerevisiae ... GAL4(855828)
human herpesvirus 2 ... HS2VP16A(1487335)
一般說明
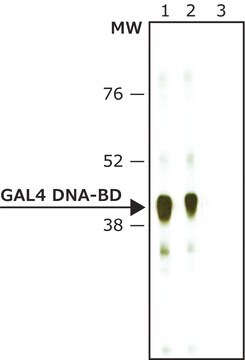
VP16 is a part of the tegument of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2) particles, and is a prototypical acidic activator. GAL4-VP16 is constructed by the fusion of the acidic activation domain of the HSV (herpes simplex virus) VP16 transactivator to the DNA binding domain of GAL4. VP16 (411-490) is the 89-residue activation domain of VP16 protein.
生化/生理作用
The GAL4 protein of yeast activates the transcription of several genes involved in galactose metabolism. This event requires that GAL4 bind to upstream activation sites with the consensus sequence 5′-CGGN5(T/A)N5CCG-3′ . A fragment of the GAL4 protein, comprising amino acids 1-147, binds DNA but fails to activate transcription. Herpes virus VP16 activates expression of immediate early genes in virally-infected cells. As most other eukaryotic transcriptional activator proteins, VP16 has a modular domain structure: it′s N-terminus is involved in DNA-protein interactions, while its C-terminal 79 amino acids have proven to be an especially potent transactivation domain. When fused to the DNA-binding domain of the yeast GAL4, this VP16 fragment functions as an activator of transcription in yeast, mammalian cells and in vitro transcription assays. VP16 has been shown to bind to TBP, TFIIB, and replication factor A.
The GAL4 yeast protein is responsible for the induction of various genes involved in galactose metabolism. This requires the binding of GAL4 gene to the upstream activation sites containing the consensus sequence 5′-CGGN5(T/A)N5CCG-3′. VP16 protein is essential for inducing the expression of viral immediate-early (IE) genes. A fragment of the GAL4 protein, comprising amino acids 1-147, binds DNA but fails to activate transcription. The highly acidic C-terminal tail of VP16 functions as a potent transcriptional activator in mammalian cells. GAL4-VP16 construct functions as an activator which promotes transcription in mammalian cells.
外觀
Clear and colorless frozen liquid solution
準備報告
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. While working, please keep sample on ice.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells.
Sadowski I and Ptashne M
Nucleic Acids Research, 17(18) (1989)
Large-scale chromatin unfolding and remodeling induced by VP16 acidic activation domain.
Tumbar T, et al.
The Journal of Cell Biology, 145(7), 1341-1354 (1999)
Hydrophobic cluster analysis predicts an amino-terminal domain of varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 10 required for transcriptional activation.
Moriuchi H, et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 92(20), 9333-9337 (1995)
L Keegan et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 231(4739), 699-704 (1986-02-14)
The yeast GAL4 protein (881 amino acids) binds to specific DNA sites upstream of target genes and activates transcription. Derivatives of this protein bearing as few as 74 amino terminal residues bind to these sites but fail to activate transcription.
A synergistic increase in potency of a multimerized VP16 transcriptional activation domain.
Emami KH1 and Carey M.
The Embo Journal, 11(13), 5005-5012 (1992)
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门