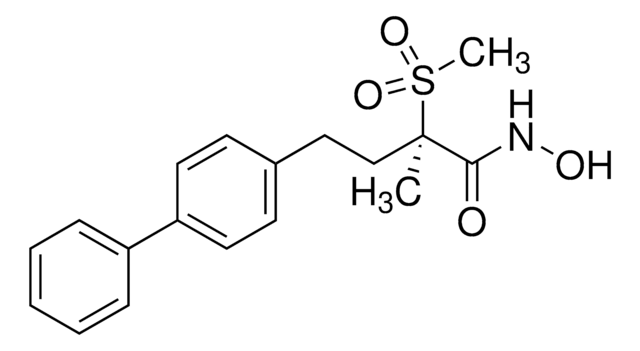
S7323
14-3-3 Sigma histidine-tagged human
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, C-terminal, ≥90% (SDS-PAGE), buffered aqueous glycerol solution
别名:
14-3-3σ, Epitheliial cell marker protein 1, HME1, Makorin, ring finger protein 3, Mkrn3, Mmel, SFN, Stratifin, Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein, sigma polypeptide, YWHAS
登录查看公司和协议定价
所有图片(1)
About This Item
分類程式碼代碼:
12352202
NACRES:
NA.32
推荐产品
生化/生理作用
14-3-3 proteins are involved in a multitude of biological processes and play a regulatory role in processes such as apoptotic cell death, mitogenic signal transduction, and cell cycle control. 14-3-3σ proteins play a critical role in signal transduction pathways and cell cycle regulation. 14-3-3σ is the only 14-3-3 isoform induced by the tumor suppressor protein p53, in response to γ-irradiation and other DNA-damaging agents. 14-3-3σ is a p53-regulated inhibitor of G2/M progression and acts as a tumor suppressor gene that is inactivated by methylation of its 5′ CpG islands in epithelial tumor cells.
外觀
Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, and 20% glycerol (w/v).
相關產品
产品编号
说明
价格
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Huiling Yang et al.
Cancer research, 66(6), 3096-3105 (2006-03-17)
14-3-3 sigma is induced by tumor suppressor protein p53 in response to DNA damage. p53 can directly transactivate the expression of 14-3-3 sigma to cause a G(2) cell cycle arrest when cell DNA is damaged. The expression of 14-3-3 sigma
José M A Moreira et al.
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP, 7(7), 1225-1240 (2008-04-02)
The 14-3-3 proteins constitute a family of highly conserved and broadly expressed multifunctional polypeptides that are involved in a variety of important cellular processes that include cell cycle progression, growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. Although the exact cellular function(s) of 14-3-3
H Hermeking et al.
Molecular cell, 1(1), 3-11 (1998-07-11)
Exposure of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells to ionizing radiation results in a cell-cycle arrest in G1 and G2. The G1 arrest is due to p53-mediated induction of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1/SDI1, but the basis for the G2 arrest is
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门