推荐产品
生物源
rabbit
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
IgG fraction of antiserum
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
形狀
buffered aqueous solution
分子量
antigen 65 kDa
物種活性
rat
技術
microarray: suitable
western blot: 1:5,000 using extract of rat brain membrane fraction
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... SYT1(6857)
mouse ... Syt1(20979)
rat ... Syt1(25716)
一般說明
Synaptotagmin (Syt, p65) is an abundant synaptic vesicle (SV) membrane protein. It is characterized by a short intravesicular N-terminal domain, a single transmembrane region and two copies of highly conserved internal repeats, known as the C2A and C2B domains, which are homologous to the C2 regulatory region of protein kinase C (PKC) in the cytoplasmic domain. At least eight different isoforms of synaptotagmin (SytI-VIII) are expressed in the brain, four of which (Syt IV, V, VII and VIII) are also expressed in non-neuronal tissues.
特異性
The sequence is highly conserved among species (SytI) and is not found in other known synaptotagmin isoforms (SytII-VIII).
免疫原
synthetic peptide corresponding to N-terminus of synaptotagmin I (SytI) of rat origin (amino acids 1-16 with C-terminally added lysine), conjugated to KLH.
應用
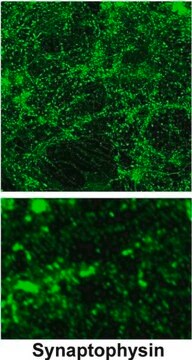
Anti-Synaptotagmin antibody produced in rabbit has been used:
- for cell surface labelling of synaptotagmin I (SytI)
- in immunofluorescence microscopy
- in western blotting
生化/生理作用
Synaptotagmin binds Ca2+ phospholipids with high affinity and has a central role in Ca2+ regulated neurotransmitter release. Synaptotagmin functions as a Ca2+ sensor and is required for efficient exocytosis, particularly in the vesicle docking and/or fusion step with the plasma membrane. Ca2+ influx triggers synaptotagmin to interact with either syntaxin or SNAP-25 and the cytoplasmic domain of neurexin leading to fusion and exocytosis. Mutations or deletion of synaptotagmin result in severely impaired Ca2+ triggered neurotransmitter release. Synapses of SytI knockout mice lack the fast-component of Ca2+ dependent neurotransmitter release, but exhibit no changes in the slow, Ca2+ independent component of synaptic vesicle exocytosis.
外觀
0.01M 磷酸缓冲盐溶液,pH 7.4,含 15mM 叠氮化钠。
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
nwg
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Tumor protein D52 controls trafficking of an apical endolysosomal secretory pathway in pancreatic acinar cells
Messenger SW, et al.
American Journal of Physiology: Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 305(6), G439-G452 (2013)
The products of the Drosophila stoned locus interact with synaptic vesicles via synaptotagmin
Phillips AM, et al.
The Journal of Neuroscience, 20(22), 8254-8261 (2000)
Expression, localization, and functional role for synaptotagmins in pancreatic acinar cells
Falkowski MA, et al.
American Journal of Physiology: Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 301(2), G306-G316 (2011)
Michelle A Falkowski et al.
American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology, 301(2), G306-G316 (2011-06-04)
Secretagogue-induced changes in intracellular Ca(2+) play a pivotal role in secretion in pancreatic acini yet the molecules that respond to Ca(2+) are uncertain. Zymogen granule (ZG) exocytosis is regulated by soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) complexes. In nerve
Gui-Hai Chen et al.
Neurobiology of aging, 28(4), 611-618 (2006-05-09)
The age-related decline of learning and memory is a common phenomenon in humans and animals, even though the underlying mechanism is not yet known. In the present study, we propose that synaptotagmin 1 (Syt 1) might be a synaptic protein
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门