推荐产品
品質等級
化驗
≥98%
形狀
powder
技術
HPLC: suitable
顏色
white to off-white
mp
159-162 °C (lit.)
SMILES 字串
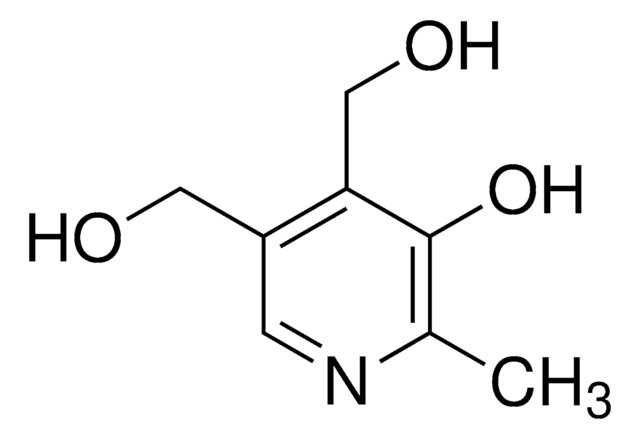
Cc1ncc(CO)c(CO)c1O
InChI
1S/C8H11NO3/c1-5-8(12)7(4-11)6(3-10)2-9-5/h2,10-12H,3-4H2,1H3
InChI 密鑰
LXNHXLLTXMVWPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
基因資訊
human ... CYP1A2(1544)
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
一般說明
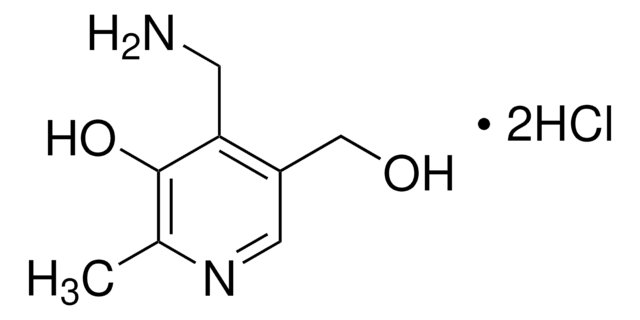
吡哆醇(维生素B6)是维生素B6的一种形式。其他形式包括醛吡哆醛和酰胺吡哆胺。它是新陈代谢的重要辅助因子。
维生素B族可溶于水溶性,有六种形式,包括吡哆醛、吡哆辛、吡哆胺、吡哆胺5′-磷酸酯、吡哆醇5′-磷酸酯和吡哆醛5′-磷酸酯。维生素B6 分布于坚果、全谷物和动物肉类中。
應用
吡哆醇在细胞培养和其他应用中被用作磷酸吡哆醛的前体。它已在RP-HPLC(反相高效液相色谱)方法中被用作标准品。吡哆醇已被作为膳食补充剂,用于研究大鼠的脂质特征。
吡哆醇已用作以下物质的组分:
- 甘蔗蚜虫的人工饲料
- 改性Strullu和Romand培养基(MSR),用于胡萝卜根器官培养
- 大肠杆菌培养基的Luria 肉汤
生化/生理作用
吡哆醇在细胞维护和氨基酸代谢中起着关键作用。缺乏维生素B6会导致贫血,尤其是孕妇,还会导致新生儿癫痫发作。它在δ-氨基乙酰酸形成过程、γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)转氨酶和谷氨酸脱羧酶中用作血红素生物合成的辅助因子。维生素B6还有助于清除活性氧(ROS),帮助植物克服非生物和生物胁迫。
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 2
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
其他客户在看
An artificial diet for the sugarcane aphid (Melanaphis sacchari Zehntner)(Hemiptera: Aphididae) with potential uses for in vitro toxicological studies
Toledo-Hernandez E, et al.
Florida entomologist, 101(3), 395-399 (2018)
Design, Validation, and Application of an Enzyme-Coupled Hydrogen Sulfide Detection Assay
Lynch MJ and Crane BR
Biochemistry, 58(6), 474-483 (2018)
Henrika Wickström et al.
AAPS PharmSciTech, 18(2), 293-302 (2016-10-16)
Printing technologies were recently introduced to the pharmaceutical field for manufacturing of drug delivery systems. Printing allows on demand manufacturing of flexible pharmaceutical doses in a personalized manner, which is critical for a successful and safe treatment of patient populations with
Tracking Lipid Transfer by Fatty Acid Isotopolog Profiling from Host Plants to Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Fungi
Redkar A, et al.
Bio-protocol, 8(7) (2018)
E B Rimm et al.
JAMA, 279(5), 359-364 (1998-02-12)
Hyperhomocysteinemia is caused by genetic and lifestyle influences, including low intakes of folate and vitamin B6. However, prospective data relating intake of these vitamins to risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) are not available. To examine intakes of folate and
实验方案
Separation of Pyridoxine; Nicotinamide; Nicotinic acid; Folic acid; (−)-Riboflavin, meets USP testing specifications; L-Ascorbic acid
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门