推荐产品
重組細胞
expressed in E. coli
品質等級
化驗
≥90% (SDS-GE)
形狀
buffered aqueous solution
分子量
45,541.2 Da
溶解度
water: soluble
運輸包裝
ambient
儲存溫度
−20°C
一般說明
Research area: Cell Struc
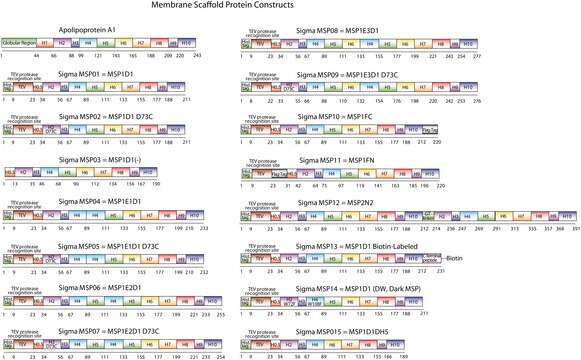
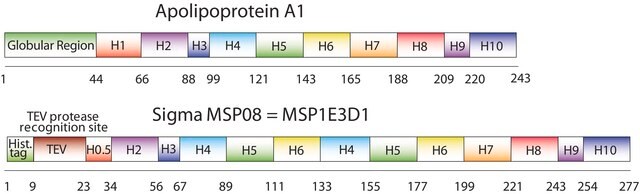
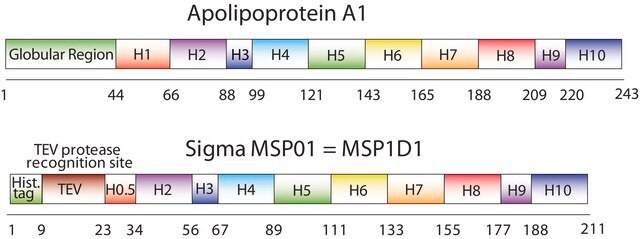
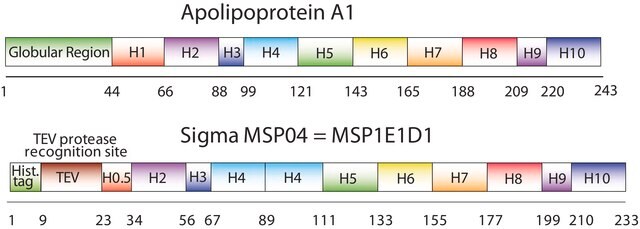
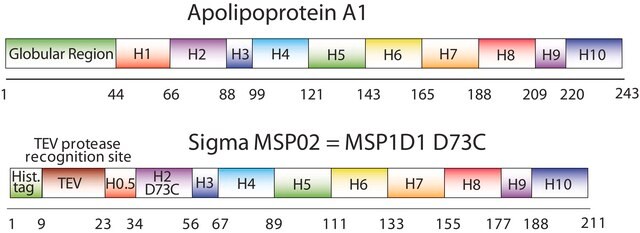
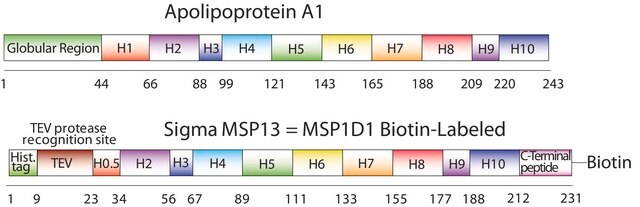
The first MSP, MSP1, was engineered with its sequence based on the sequence of A-1 but without the globular N-terminal domain of native A-1. The Membrane Scaffold Protein 1D1 (MSP1D1) variant of MSP1 deletes the first 11 amino acids in the Helix 1 portion (referred to as “H0.5” in the accompanying figure) of the original MSP1 sequence. Membrane Scaffold Protein 2N2 (MSP 2N2) is a fusion of MSP1D1 and another MSP variant, MSP1D2. MSP1D2 deletes the first 22 amino acids of the original MSP sequence (i.e. the entire H1 segment). In MSP2N2, a GT linker connects MSP1D1 and MSP1D2.
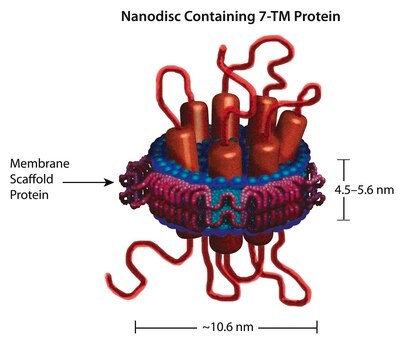
Nanodisc technology is an approach rendering membrane proteins soluble in aqueous solutions in a native-like bilayer environment, where the membrane proteins remain stable and active. The Nanodisc concept is derived from high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles and their primary protein component, apolipoprotein. The Nanodisc is a non-covalent structure of phospholipid bilayer and membrane scaffold protein (MSP), a genetically engineered protein that mimics the function of Apolipoprotein A-1 (ApoA-1).
The first MSP, MSP1, was engineered with its sequence based on the sequence of A-1 but without the globular N-terminal domain of native A-1. The Membrane Scaffold Protein 1D1 (MSP1D1) variant of MSP1 deletes the first 11 amino acids in the Helix 1 portion (referred to as “H0.5” in the accompanying figure) of the original MSP1 sequence. Membrane Scaffold Protein 2N2 (MSP 2N2) is a fusion of MSP1D1 and another MSP variant, MSP1D2. MSP1D2 deletes the first 22 amino acids of the original MSP sequence (i.e. the entire H1 segment). In MSP2N2, a GT linker connects MSP1D1 and MSP1D2.
Nanodisc technology is an approach rendering membrane proteins soluble in aqueous solutions in a native-like bilayer environment, where the membrane proteins remain stable and active. The Nanodisc concept is derived from high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles and their primary protein component, apolipoprotein. The Nanodisc is a non-covalent structure of phospholipid bilayer and membrane scaffold protein (MSP), a genetically engineered protein that mimics the function of Apolipoprotein A-1 (ApoA-1).
應用
Membrane Scaffold Protein 2N2 has been used in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and for reconstitution of human β3 homopentameric gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor (GABAAR) in nanodiscs.
生化/生理作用
Scaffold proteins play a crucial role in providing specificity to the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, which is essential for normal cellular functions and development. They help regulate the localization of MAPK components, allowing for targeted modulation of cellular responses without affecting global MAPK activity.
法律資訊
Nanodisc technology, and many of its uses, are covered by the following patents held by the University of Illinois.
- 7,691,414 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,662,410 Membrane scaffold proteins and embedded membrane proteins
- 7,622,437 Tissue factor compositions and methods
- 7,592,008 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,575,763 Membrane scaffold proteins and tethered membrane proteins
- 7,083,958 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,048,949 Membrane scaffold proteins
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 2
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
其他客户在看
Tomasz Uchański et al.
Nature methods, 18(1), 60-68 (2021-01-08)
Nanobodies are popular and versatile tools for structural biology. They have a compact single immunoglobulin domain organization, bind target proteins with high affinities while reducing their conformational heterogeneity and stabilize multi-protein complexes. Here we demonstrate that engineered nanobodies can also
实验方案
The following material related to Nanodisc Technology is adapted from on-line content of the research group of Professor Stephen Sligar of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, with the kind permission of Professor Sligar.
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门