推荐产品
形狀
powder
mp
279-281 °C (lit.)
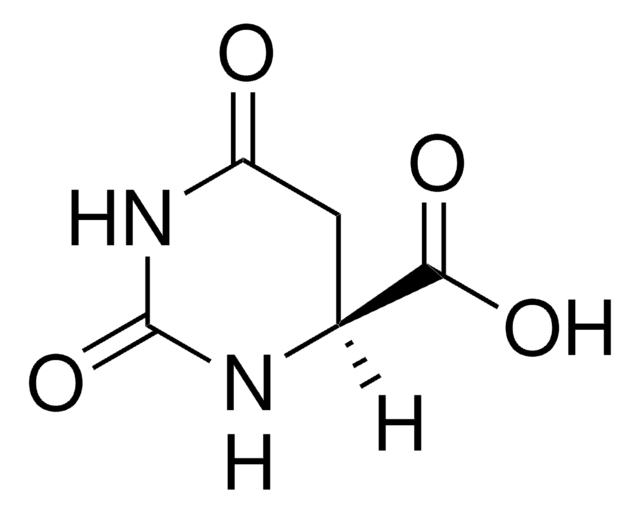
SMILES 字串
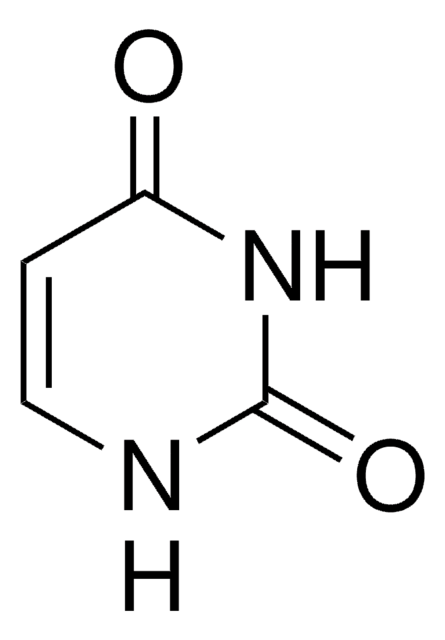
O=C1CCNC(=O)N1
InChI
1S/C4H6N2O2/c7-3-1-2-5-4(8)6-3/h1-2H2,(H2,5,6,7,8)
InChI 密鑰
OIVLITBTBDPEFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
一般說明
Dihydrouracil (DiHU) is a minor base found in transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA). It is similar to uracil with the only exception that the C5-C6 bond is saturated. It crystallized in the monoclinic system with space group P21/C. Its crystalline structure has been analyzed. Its generation from L-cysteine and uracil via photochemical addition has been described.
應用
Dihydrouracil has been used as a standard for ureido group in the colorimentric assay of transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA).
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
其他客户在看
Teresa Di Desidero et al.
Investigational new drugs, 36(4), 709-714 (2018-03-01)
The aim of the present study was to assess the pharmacokinetics (PK) of metronomic capecitabine and its metabolites in a population of refractory metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients. Thirty-four patients (M/F, 22/12) with a diagnosis of mCRC received capecitabine 800 mg
Jihane Basbous et al.
Nucleic acids research, 48(4), 1886-1904 (2019-12-20)
Imbalance in the level of the pyrimidine degradation products dihydrouracil and dihydrothymine is associated with cellular transformation and cancer progression. Dihydropyrimidines are degraded by dihydropyrimidinase (DHP), a zinc metalloenzyme that is upregulated in solid tumors but not in the corresponding
Stereochemistry of nucleic acids and their constituents. VI. The crystal structure and conformation of dihydrouracil: a minor base of transfer-ribonucleic acid.
Rohrer DC and Sundaralingam M.
Acta Crystallographica Section B, Structural Science, 26(5), 546-553 (1970)
Cuiping Liu et al.
Methods in enzymology, 469, 69-93 (2009-01-01)
Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules mediate translation of the nucleic acid genetic code into the amino acid building blocks of proteins, thus ensuring the survivability of cells. The dynamic properties of tRNA molecules are crucial to their functions in both activity
M Boisdron-Celle et al.
Cancer letters, 249(2), 271-282 (2006-10-27)
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU)-related early toxicity, due to a metabolic deficiency, is rare but is potentially severe and even lethal (0.1%). It is due to dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD) gene polymorphism or some epigenetic factors. The detection of metabolic change could prevent severe
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门