C1200000
氯霉素,大包装
European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
别名:
D-(−)-苏-2,2-二氯-N-[β-羟基-α-(羟甲基)-β-(4-硝基苯基)乙基]乙酰胺, D-(−)-苏-2-二氯乙酰胺基-1-(4-硝基苯基)-1,3-丙二醇, D-苏-2,2-二氯-N-β[-羟基-α-(羟甲基)-4-硝基苯乙基]乙酰胺, 氯霉素
登录查看公司和协议定价
所有图片(1)
About This Item
线性分子式:
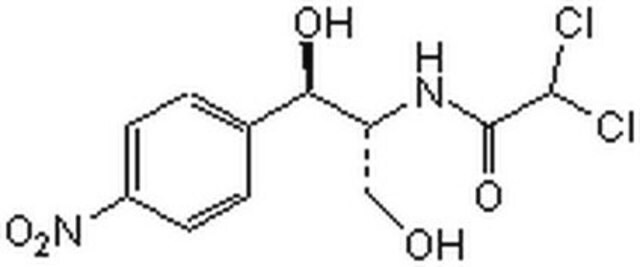
Cl2CHCONHCH(CH2OH)CH(OH)C6H4NO2
CAS号:
分子量:
323.13
Beilstein:
2225532
MDL號碼:
分類程式碼代碼:
41116107
PubChem物質ID:
NACRES:
NA.24
推荐产品
等級
pharmaceutical primary standard
API 家族
chloramphenicol
製造商/商標名
EDQM
mp
149-153 °C (lit.)
應用
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
形式
neat
SMILES 字串
OC[C@@H](NC(=O)C(Cl)Cl)[C@H](O)c1ccc(cc1)[N+]([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C11H12Cl2N2O5/c12-10(13)11(18)14-8(5-16)9(17)6-1-3-7(4-2-6)15(19)20/h1-4,8-10,16-17H,5H2,(H,14,18)/t8-,9-/m1/s1
InChI 密鑰
WIIZWVCIJKGZOK-RKDXNWHRSA-N
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
一般說明
This product is provided as delivered and specified by the issuing Pharmacopoeia. All information provided in support of this product, including SDS and any product information leaflets have been developed and issued under the Authority of the Issuing Pharmacopoeia. For further information and support please go to the website of the issuing Pharmacopoeia.
應用
Chloramphenicol EP Reference standard, intended for use in laboratory tests only as specifically prescribed in the European Pharmacopoeia.
生化/生理作用
作用机制:氯霉素通过与50S核糖体亚基结合并阻止氨酰基tRNA附着于核糖体来阻断肽基转移酶步骤,从而抑制细菌蛋白质的合成。 它还抑制线粒体和叶绿体蛋白的合成以及(p)ppGpp的核糖体形成,从而抑制rRNA的转录。
耐药性机制:使用氯霉素乙酰转移酶会使产物乙酰化并使其失活。
抗菌谱:这是一种针对革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性细菌的广谱抗生素,主要用于眼科和兽医目的。
耐药性机制:使用氯霉素乙酰转移酶会使产物乙酰化并使其失活。
抗菌谱:这是一种针对革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性细菌的广谱抗生素,主要用于眼科和兽医目的。
包裝
The product is delivered as supplied by the issuing Pharmacopoeia. For the current unit quantity, please visit the EDQM reference substance catalogue.
其他說明
Sales restrictions may apply.
相關產品
产品编号
说明
价格
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Carc. 2 - Eye Dam. 1 - Repr. 2
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
其他客户在看
Anthony J Brzoska et al.
PloS one, 8(2), e56090-e56090 (2013-02-15)
Members of the genus Acinetobacter have been the focus recent attention due to both their clinical significance and application to molecular biology. The soil commensal bacterium Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1 has been proposed as a model system for molecular and genetic
Shunichi Takahashi et al.
Plant physiology, 161(1), 477-485 (2012-11-22)
A moderate increase in seawater temperature causes coral bleaching, at least partially through photobleaching of the symbiotic algae Symbiodinium spp. Photobleaching of Symbiodinium spp. is primarily associated with the loss of light-harvesting proteins of photosystem II (PSII) and follows the
Uwe Richter et al.
Current biology : CB, 23(6), 535-541 (2013-03-05)
Proliferating cells require coordinated gene expression between the nucleus and mitochondria in order to divide, ensuring sufficient organelle number in daughter cells [1]. However, the machinery and mechanisms whereby proliferating cells monitor mitochondria and coordinate organelle biosynthesis remain poorly understood.
J N de Almeida Júnior et al.
Clinical microbiology and infection : the official publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 20(8), 784-790 (2013-12-21)
Trichosporon spp. have recently emerged as significant human pathogens. Identification of these species is important, both for epidemiological purposes and for therapeutic management, but conventional identification based on biochemical traits is hindered by the lack of updates to the species
David G Kirk et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 80(16), 5141-5150 (2014-06-15)
Clostridium botulinum produces heat-resistant endospores that may germinate and outgrow into neurotoxic cultures in foods. Sporulation is regulated by the transcription factor Spo0A and the alternative sigma factors SigF, SigE, SigG, and SigK in most spore formers studied to date.
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系客户支持