推荐产品
生物源
mouse
品質等級
抗體表格
purified immunoglobulin
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
TAP 952, monoclonal
物種活性
human, sheep, sea urchin, porcine, mouse, Drosophila, snail
技術
dot blot: suitable
immunofluorescence: suitable
western blot: suitable
同型
IgG1κ
運輸包裝
wet ice
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... TUBA1A(7846)
一般說明
已经在真核细胞中鉴定了微管蛋白的几种翻译后修饰。 糖基化是一种多修饰,其发生在纤毛草履虫的轴丝微管蛋白中鉴定的可变长度的甘氨酸链的侧向分支中。已经在许多单细胞和多细胞生物的微管蛋白和/或纤毛/鞭毛上检测到这种修饰。草履虫的细胞质和轴突区室之间不同的聚糖基化微管蛋白亚型的差异分布表明微管蛋白的聚糖基化水平在细胞水平上受到高度调节。在草履虫中,TAP 952抗体对细胞质和轴突微管蛋白具有反应性。在后生细胞和/或细胞系中,它对运动性纤毛和原发纤毛的微管蛋白具有特异性,因此可用于运动性纤毛和原发纤毛的检测。
特異性
该抗体可识别单糖基化的α和β微管蛋白的C末端。
可用作活动性纤毛的标志物。
可用作活动性纤毛的标志物。
免疫原
电洗脱草履虫轴丝微管蛋白
表位:单糖基化的α-微管蛋白的氨基酸427-449和单糖基化的β-微管蛋白的氨基酸427-442(Bré et al., 1998, Mol.Biol. Cell 9, 2655-2665)
應用
使用该小鼠单克隆抗体(抗单糖基化微管蛋白抗体,克隆TAP 952,经验证可用于蛋白质印迹法和免疫荧光&斑点印迹法)检测微管蛋白。
免疫荧光分析:一个来自独立实验室的代表性批次在小鼠精子中检测到单糖基化微管蛋白(Bre,M.H.,et al.(1996).J Cell Sci. (Pt 4):727-738.)。
斑点印迹分析:一个来自独立实验室的代表性批次在合成单糖基化微管蛋白肽中检测到单糖基化微管蛋白(Bre,M.H.,et al.(1996).J Cell Sci. (Pt 4):727-738.)。
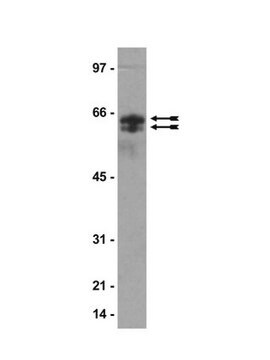
蛋白质印迹分析:一个来自独立实验室的代表性批次在一组选定物种的总蛋白提取物中检测到单糖基化微管蛋白(Bre,M.H.,et al.(1996).J Cell Sci.(Pt 4):727-738.)。
免疫荧光分析:一个来自独立实验室的代表性批次在狐猴、人和海胆精子中检测到单糖基化微管蛋白(Bre,M.H.,et al.(1996).J Cell Sci.(Pt 4):727-738.)。
斑点印迹分析:一个来自独立实验室的代表性批次在合成单糖基化微管蛋白肽中检测到单糖基化微管蛋白(Bre,M.H.,et al.(1996).J Cell Sci. (Pt 4):727-738.)。
蛋白质印迹分析:一个来自独立实验室的代表性批次在一组选定物种的总蛋白提取物中检测到单糖基化微管蛋白(Bre,M.H.,et al.(1996).J Cell Sci.(Pt 4):727-738.)。
免疫荧光分析:一个来自独立实验室的代表性批次在狐猴、人和海胆精子中检测到单糖基化微管蛋白(Bre,M.H.,et al.(1996).J Cell Sci.(Pt 4):727-738.)。
研究子类别
一般翻译后修饰
一般翻译后修饰
研究类别
信号传导
信号传导
品質
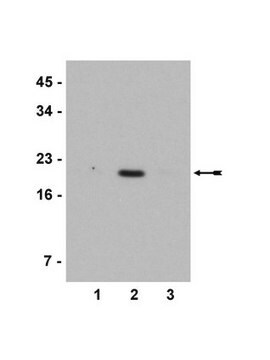
通过蛋白质印迹法对草履虫总细胞骨架提取物进行评估。
蛋白质印迹分析:该抗体以1:50,000稀释度在10 µg草履虫总细胞骨架蛋白中检测到单糖基化微管蛋白。
蛋白质印迹分析:该抗体以1:50,000稀释度在10 µg草履虫总细胞骨架蛋白中检测到单糖基化微管蛋白。
標靶描述
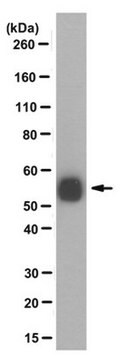
观测分子量〜50 kDa
外觀
形式:纯化
纯化的小鼠单克隆IgG1κ,溶于含0.1 M Tris-甘氨酸(pH 7.4)、150 mM NaCl和0.05%叠氮化钠的缓冲液中。
纯化蛋白G
儲存和穩定性
自接收之日起,在2-8°C下可稳定保存1年。
其他說明
浓度:关于批次特定浓度请参见检验报告。
免責聲明
除非我们的目录或产品随附的其他公司文件中另有说明,否则我们的产品预期仅用于研究用途,不得用于任何其他目的,包括但不限于未经授权的商业用途、体外诊断用途、离体或体内治疗用途或对人类或动物的任何类型的消费或应用。
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
K Million et al.
Journal of cell science, 112 ( Pt 23), 4357-4366 (1999-11-24)
Tubulins are the major proteins within centriolar and axonemal structures. In all cell types studied so far, numerous alpha- and beta-tubulin isoforms are generated both by expression of a multigenic family and various post-translational modifications. We have developed a primary
Polyglycylation of tubulin: a posttranslational modification in axonemal microtubules.
Redeker, V, et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 266, 1688-1691 (1994)
Krzysztof Rogowski et al.
Cell, 137(6), 1076-1087 (2009-06-16)
Polyglycylation is a posttranslational modification that generates glycine side chains on proteins. Here we identify a family of evolutionarily conserved glycine ligases that modify tubulin using different enzymatic mechanisms. In mammals, two distinct enzyme types catalyze the initiation and elongation
A M Callen et al.
Biology of the cell, 81(2), 95-119 (1994-01-01)
Ciliates are very good models for studying post-translationally generated tubulin heterogeneity because they exhibit highly differentiated microtubular networks in combination with reduced genetic diversity. We have approached the analysis of tubulin heterogeneity in Paramecium through extensive isolation and characterization of
Dorota Wloga et al.
Developmental cell, 16(6), 867-876 (2009-06-18)
In most ciliated cell types, tubulin is modified by glycylation, a posttranslational modification of unknown function. We show that the TTLL3 proteins act as tubulin glycine ligases with chain-initiating activity. In Tetrahymena, deletion of TTLL3 shortened axonemes and increased their
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门