推荐产品
生物源
rat
品質等級
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
purified antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
B6A6, monoclonal
純化經由
using protein G
物種活性
mouse
包裝
antibody small pack of 100 μg
技術
flow cytometry: suitable
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): suitable
同型
IgG2aκ
表位序列
Unknown
Protein ID登錄號
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
ambient
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
一般說明
The small intestine consists of continuous villi and crypts. The crypt is mainly a proliferative compartment and is maintained by multipotent stem cells whereas the villus represents the differentiated compartment, and it receives cells from multiple crypts. The functional compartment of the epithelium contains differentiated cells that populate the villi and can be categorized based on their function: enterocytes that function to absorb nutrients, goblet cells that secrete a protective mucus barrier, and enteroendocrine cells that release gastrointestinal hormones. Intestinal crypts contain intestinal stem cells (ISC), which are multipotent adult stem cells that reside in the base of crypts. They continuously self-renew by dividing and differentiate into the specialized cells of the intestinal epithelium, which renews throughout life. ISCs located either at the crypt base interspersed between the Paneth cells can be categorized into active-cycling (Lgr5+ cells) or those located near the þ4 position in the crypt as slow-cycling Bmi-1+ cells. Paneth cells that are responsible for secreting antibacterial peptides reside at the base of the proliferative compartment. As ISCs begin to differentiate, they migrate toward the lumen and are eventually shed, either from the tip of the intestinal villi or from the surface of the colonic epithelium. Villus represents the differentiated compartment of intestinal cells. Clone B6A6 recognizes most villous cells except goblet cells. (Ref.: Smith, NR., et al. (2018). Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6(1);79-96; Wang, F., et al. (2013). Gastroenterology. 145(2); 383-395; Umar, S. (2010). Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 12(5); 340-348).
特異性
Clone B6A6 is a rat monoclonal antibody that detects intestinal villus cells.
免疫原
Undifferentiated Mouse intestinal epithelial cells. Rats were preimmunized with isolations of differentiated mouse intestinal epithelial cells and then treated with cyclophosphamide (i.p.) to eliminate B lymphocytes reacting against these antigens. Subsequent immunization was with crypt-based single cells.
應用
Quality Control Testing
Isotype testing: Identity Confirmation by Isotyping Test.
Isotyping Analysis: The identity of this monoclonal antibody is confirmed by isotyping test to be mouse IgG2a .
Tested Applications
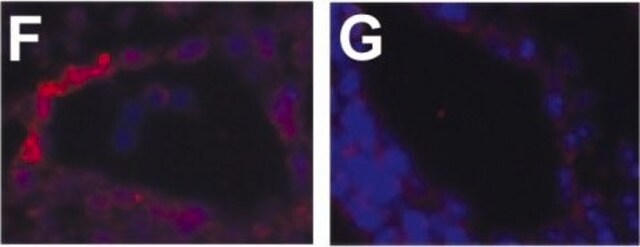
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot detected Intestinal Villus in Lgr5-GFP mouse intestinal cells ( Data courtesy of Prof. Melissa Wong, Ph.D., Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, Oregon USA).
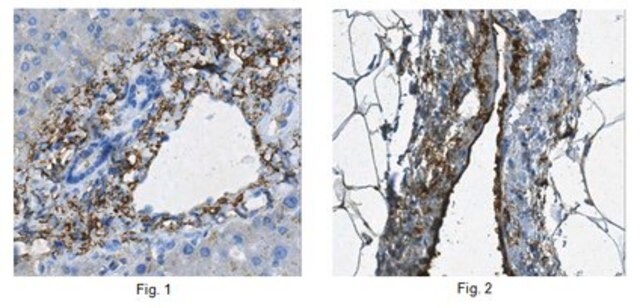
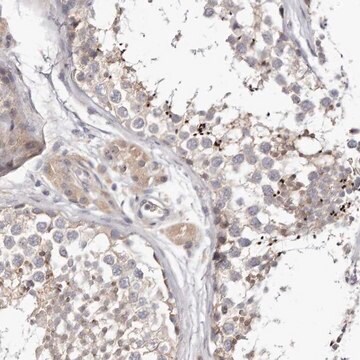
Immunohistochemistry Applications: A representative lot detected Intestinal Villus cells in Immunohistochemistry applications (Wang, F., et al. (2013). Gastroenterology. 145(2): 383-95.e1-21).
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot detected Intestinal Villus in Flow Cytometry applications (Wang, F., et al. (2013). Gastroenterology. 145(2): 383-95.e1-21; Smith, N.R., et al. (2017). Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3(3): 389-409; Yan, K.S., et al. (2017). Cell Stem Cell. 21(1):7 8-90.e6; Smith, N.R., et al. (2018). Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6(1): 79-96).
Note: Actual optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user as specimens, and experimental conditions may vary with the end user
Isotype testing: Identity Confirmation by Isotyping Test.
Isotyping Analysis: The identity of this monoclonal antibody is confirmed by isotyping test to be mouse IgG2a .
Tested Applications
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot detected Intestinal Villus in Lgr5-GFP mouse intestinal cells ( Data courtesy of Prof. Melissa Wong, Ph.D., Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, Oregon USA).
Immunohistochemistry Applications: A representative lot detected Intestinal Villus cells in Immunohistochemistry applications (Wang, F., et al. (2013). Gastroenterology. 145(2): 383-95.e1-21).
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot detected Intestinal Villus in Flow Cytometry applications (Wang, F., et al. (2013). Gastroenterology. 145(2): 383-95.e1-21; Smith, N.R., et al. (2017). Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3(3): 389-409; Yan, K.S., et al. (2017). Cell Stem Cell. 21(1):7 8-90.e6; Smith, N.R., et al. (2018). Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6(1): 79-96).
Note: Actual optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user as specimens, and experimental conditions may vary with the end user
Anti-Intestinal Villus clone B6A6, Cat. No. MABS2233, is a rat monoclonal antibody that detects Intestinal Villus cells and is tested for use in and Flow Cytometry and Immunohistochemistry.
外觀
Purified rat monoclonal antibody IgG2a in buffer containing 0.1 M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl with 0.05% sodium azide.
儲存和穩定性
Recommended storage: +2°C to +8°C.
其他說明
Concentration: Please refer to the Certificate of Analysis for the lot-specific concentration.
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门