推荐产品
生物源
hamster (Armenian)
品質等級
抗體表格
purified antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
Nilo2, monoclonal
物種活性
mouse
技術
flow cytometry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
inhibition assay: suitable
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): suitable
western blot: suitable
運輸包裝
ambient
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
一般說明
Similar to other cell types, neural cells are generated from primary progenitor cells known as type B astrocytes or neural stem cells (NSCs) via stages of amplification (transient amplifying cells), resulting in the generation of intermediate precursor cells (iPCs) committed to neurons (nIPCs), astrocytes (aIPCs), or oligodendrocytes (oIPCs). In adult rodent brain, NSCs and iPCs are mainly restricted to niches in the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricles (LV). In the adult SVZ, type B cells (SVZB) generate neuroblasts (type A cells, neuronal precursors) through a highly proliferative transit amplifying population (type C cells). NSCs and iPCs paly important roles in neurogenesis in the adult brain. Neuroblasts, for example, are known to migrate from their SVZ niche through the rostral migratory stream (RMS) to the olfactory bulb for the continuous generation of periglomerular interneurons. In addition to maintaining the homeostasis of the olfactory bulb, both neuroblasts and NSCs are shown to mobilize from their SVZ niches to various brain damage sites caused by tumor growth, cryolesion, focal demyelinization, and mechanical lesion.
特異性
Nilo (Neural Identification Lineage from Olfactory bulb) monoclonal antibody Nilo2 (Cat. No. MABD402) targets neuroblasts (Elvira, G., et al. (2012). PLoS One. 7(9):e44466), while Nilo1 (Cat. No. MABD401) recognizes neural stem cells (NSCs; type B astrocytes) in adult mouse brain and radial glia in mouse embryo (Elvira, G., et al. (2015). Stem Cell Res. 14(1):114-129). Clone Nilo1 identified early progenitor cells (Sox2+, EGFR+, GFAP+ and vimentin+), whereas Nilo2 identified more differentiated neural progenitor cells committed to the neuroblast pathway (Tuj-1+, PSA-NCAM+ and DCX+). Nilo1 and Nilo2 arrest neurosphere proliferation in vitro and interfered with their differentiation into mature neural cells by targeting different surface glycoproteins highly relevant on neural stem/early progenitor cell biology (Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
免疫原
E13.5 FVB mouse embryo olfactory bulb-derived neurospheres (Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
應用
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Analysis: A representative lot, when coupled to magnetic glyconanoparticles (mGNPs) and injected in mice, allowed the tracking of labelled neuroblasts migrating from their niches towards brain injury sites by MRI (Elvira, G., et al. (2015). Stem Cell Res. 14(1):114-129; Elvira, G., et al. (2012). PLoS One. 7(9):e44466).
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot, coupled to magnetic glyconanoparticles (mGNPs) or not, immunostained the surface of SVZ neurosphere-derived single cells (Elvira, G., et al. (2012). PLoS One. 7(9):e44466).
Flow Cytometry Analysis: Clone Nilo2 hybridoma culture supernatant stained the surface of 98% and 95% neurosphere-derived cells from mouse embryo olfactory bulb (OB) and adult mouse subventricular zone (SVZ), respectively (Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: Representative lot immunostained early neural precursor cells by fluorescent immunocytochemistry staining of cultured neurospheres or neurosphere-derived single cells fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. Unlike Nilo1 (Cat. No. MABD401), a small percentage of cells retained Nilo2 immunoreactivity even 7 days after differentiation induction by EGF and bFGF withdrawal in neurosphere cultures (Elvira, G., et al. (2012). PLoS One. 7(9):e44466; Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Immunofluorescence Analysis: Representative lots, when injected in mice, allowed the detection of labelled neuroblasts migrating towards brain injury sites due to CT-2A tumor growth or mechanical damage via stereotaxic PBS injection (Elvira, G., et al. (2015). Stem Cell Res. 14(1):114-129; Elvira, G., et al. (2012). PLoS One. 7(9):e44466).
Immunofluorescence Analysis: Representative lots immunostained post-mitotic neuronal precursors (e.g. type 1 neuroblasts), whereas Nilo1 (Cat. No. MABD401) stained quiescent neural progenitor cells in subventricular zone (SVZ) by fluorescent immunohistochemistry using 4% paraformaldehyde-fixed adult mouse floating sections (Elvira, G., et al. (2015). Stem Cell Res. 14(1):114-129; Elvira, G., et al. (2012). PLoS One. 7(9):e44466; Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot immunostained the thin layer of cells in the periventricular area inside the anterior SVZ (SVZa) at the beginning of the RMS, distinct from the small cell population lining the SVZ ventricle stained by Nilo1 (Cat. No. MABD401). Both Nilo1 and Nilo2 stained ependymal and subependymal layers in adult mouse olfactory bulb core, neither clone stained dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus (Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipitated a ~150-170 kDa glycoprotein from neurosphere cell membrane extracts and from SVZ neurosphere cell lysates (Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Inhibition Analysis: A representative lot inhibited the differentiation of adult mice SVZ-derived neurospheres in culture as well as the proliferation of neurosphere-derived single cells (Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected a ~150-170 kDa glycoprotein in the immunoprecipitates obtained by clone Nilo2 from neurosphere cell membrane extracts and from SVZ neurosphere cell lysates (Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot, coupled to magnetic glyconanoparticles (mGNPs) or not, immunostained the surface of SVZ neurosphere-derived single cells (Elvira, G., et al. (2012). PLoS One. 7(9):e44466).
Flow Cytometry Analysis: Clone Nilo2 hybridoma culture supernatant stained the surface of 98% and 95% neurosphere-derived cells from mouse embryo olfactory bulb (OB) and adult mouse subventricular zone (SVZ), respectively (Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: Representative lot immunostained early neural precursor cells by fluorescent immunocytochemistry staining of cultured neurospheres or neurosphere-derived single cells fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. Unlike Nilo1 (Cat. No. MABD401), a small percentage of cells retained Nilo2 immunoreactivity even 7 days after differentiation induction by EGF and bFGF withdrawal in neurosphere cultures (Elvira, G., et al. (2012). PLoS One. 7(9):e44466; Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Immunofluorescence Analysis: Representative lots, when injected in mice, allowed the detection of labelled neuroblasts migrating towards brain injury sites due to CT-2A tumor growth or mechanical damage via stereotaxic PBS injection (Elvira, G., et al. (2015). Stem Cell Res. 14(1):114-129; Elvira, G., et al. (2012). PLoS One. 7(9):e44466).
Immunofluorescence Analysis: Representative lots immunostained post-mitotic neuronal precursors (e.g. type 1 neuroblasts), whereas Nilo1 (Cat. No. MABD401) stained quiescent neural progenitor cells in subventricular zone (SVZ) by fluorescent immunohistochemistry using 4% paraformaldehyde-fixed adult mouse floating sections (Elvira, G., et al. (2015). Stem Cell Res. 14(1):114-129; Elvira, G., et al. (2012). PLoS One. 7(9):e44466; Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot immunostained the thin layer of cells in the periventricular area inside the anterior SVZ (SVZa) at the beginning of the RMS, distinct from the small cell population lining the SVZ ventricle stained by Nilo1 (Cat. No. MABD401). Both Nilo1 and Nilo2 stained ependymal and subependymal layers in adult mouse olfactory bulb core, neither clone stained dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus (Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipitated a ~150-170 kDa glycoprotein from neurosphere cell membrane extracts and from SVZ neurosphere cell lysates (Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Inhibition Analysis: A representative lot inhibited the differentiation of adult mice SVZ-derived neurospheres in culture as well as the proliferation of neurosphere-derived single cells (Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected a ~150-170 kDa glycoprotein in the immunoprecipitates obtained by clone Nilo2 from neurosphere cell membrane extracts and from SVZ neurosphere cell lysates (Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
Research Category
Stem Cell Research
Stem Cell Research
This hamster monoclonal Anti-Neuroblasts Antibody, clone Nilo2, Cat. No. MABD402 is validated for use in Flow Cytometry, Immunocytochemistry, Immunohistochemistry, Immunofluorescence, Immunoprecipitation, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Inhibition, and Western Blotting.
品質
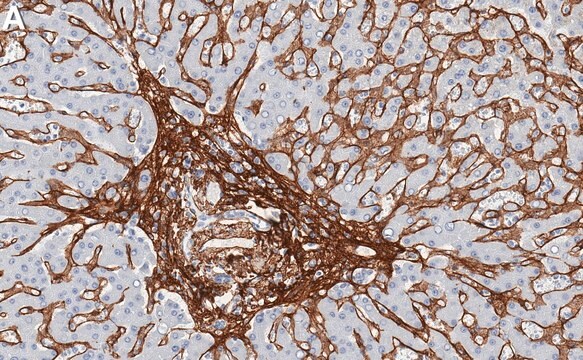
Evaluated by Immunohistochemistry in C57BL/6 mouse brain sections.
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A 1:1,000 dilution of this antibody immunostained neuroblasts in subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricle (LV) of 4% paraformaldehyde-fixed free-floating C57BL/6 mouse brain sections.
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A 1:1,000 dilution of this antibody immunostained neuroblasts in subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricle (LV) of 4% paraformaldehyde-fixed free-floating C57BL/6 mouse brain sections.
標靶描述
~150-170 kDa (glycosylated) reported (Del Valle, I., et al. (2010). Neuroscience. 169(3):1473-1485).
外觀
Protein G purified.
Format: Purified
Purified Armenian hamster monoclonal antibody in PBS without preservatives.
儲存和穩定性
Stable for 1 year at -20°C from date of receipt.
Handling Recommendations: Upon receipt and prior to removing the cap, centrifuge the vial and gently mix the solution. Aliquot into microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles, which may damage IgG and affect product performance.
Handling Recommendations: Upon receipt and prior to removing the cap, centrifuge the vial and gently mix the solution. Aliquot into microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles, which may damage IgG and affect product performance.
其他說明
Concentration: Please refer to lot specific datasheet.
免責聲明
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 2
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门