推荐产品
生物源
mouse
品質等級
抗體表格
ascites fluid
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
2B4, monoclonal
物種活性
human
製造商/商標名
Chemicon®
技術
ELISA: suitable
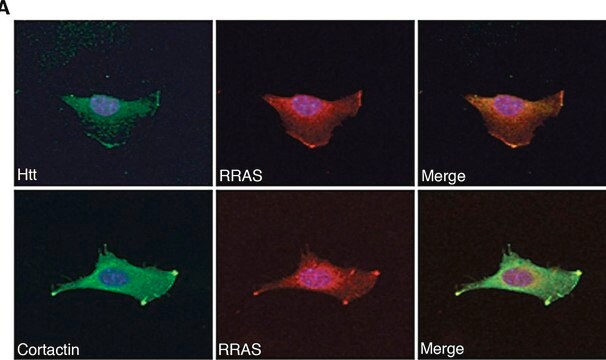
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
western blot: suitable
同型
IgG1
NCBI登錄號
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... HTT(3064) , SLC6A4(6532)
特異性
与亨廷顿蛋白(氨基酸1-82)反应。该抗体可识别野生型和突变型亨廷顿蛋白。
免疫原
表位:a.a.1-82
重组人亨廷顿蛋白,氨基酸1-82。
應用
抗-亨廷顿蛋白抗体,a.a.1-82是用于ELISA、IC、IH&WB的抗亨廷顿蛋白的抗体。
研究子类别
神经退行性疾病
神经退行性疾病
研究类别
神经科学
神经科学
蛋白质印迹:1:500-1:5,000
免疫细胞化学(1): 1:500-1:5,000
免疫组织化学(1,2): 1:500-1:5000
ELISA:1:500-1:5,000
最佳工作稀释度必须由最终用户确定。
免疫细胞化学(1): 1:500-1:5,000
免疫组织化学(1,2): 1:500-1:5000
ELISA:1:500-1:5,000
最佳工作稀释度必须由最终用户确定。
標靶描述
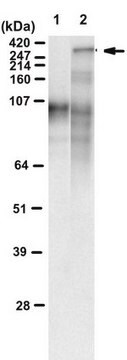
348 kDa
外觀
不含防腐剂的腹水。
未纯化
儲存和穩定性
自收到之日起在-20°C可稳定保存1年。分装保存以避免反复冻融。为了最大程度地回收产品,需在融化后和取下盖子之前将原始样品管进行离心。
分析報告
对照
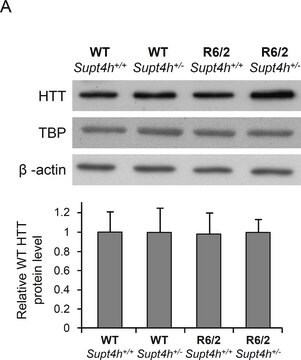
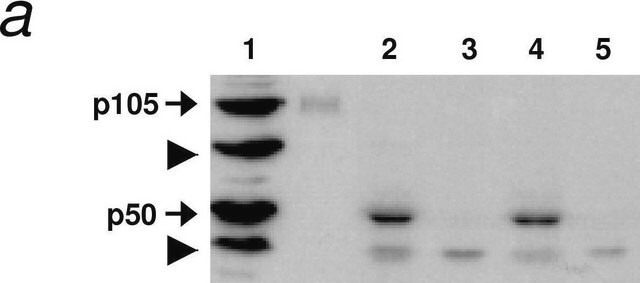
正常人大脑皮层裂解物,来自HD或野生型小鼠的小鼠大脑皮层样品
正常人大脑皮层裂解物,来自HD或野生型小鼠的小鼠大脑皮层样品
其他說明
浓度:关于批次特定浓度请参见检验报告。
法律資訊
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
免責聲明
除非我们的目录或产品随附的其他公司文件中另有说明,否则我们的产品预期仅用于研究用途,不得用于任何其他目的,包括但不限于未经授权的商业用途、体外诊断用途、离体或体内治疗用途或对人类或动物的任何类型的消费或应用。
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Acetylation targets mutant huntingtin to autophagosomes for degradation.
Hyunkyung Jeong,Florian Then,Thomas J Melia,Joseph R Mazzulli,Libin Cui,Jeffrey N Savas et al.
Cell null
Jonathan H Fox et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 286(20), 18320-18330 (2011-04-02)
Huntington disease (HD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder caused by expression of polyglutamine-expanded mutant huntingtin protein (mhtt). Most evidence indicates that soluble mhtt species, rather than insoluble aggregates, are the important mediators of HD pathogenesis. However, the differential roles of
Xiaofeng Gu et al.
Neuron, 85(4), 726-741 (2015-02-11)
The nucleus is a critical subcellular compartment for the pathogenesis of polyglutamine disorders, including Huntington's disease (HD). Recent studies suggest the first 17-amino-acid domain (N17) of mutant huntingtin (mHTT) mediates its nuclear exclusion in cultured cells. Here, we test whether
Inducing huntingtin inclusion formation in primary neuronal cell culture and in vivo by high-capacity adenoviral vectors expressing truncated and full-length huntingtin with polyglutamine expansion.
Bin Huang, Johannes Schiefer, Christian Sass, Christoph M Kosinski, Stefan Kochanek
The journal of gene medicine null
The composition of the polyglutamine-containing proteins influences their co-aggregation properties.
Bak D, Milewski M
Cell Biology International null
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门