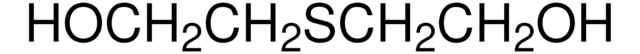推荐产品
产品名称
抗胆碱乙酰基转移酶(ChAT)抗体, serum, Chemicon®
生物源
rabbit
品質等級
抗體表格
serum
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
物種活性
mouse, human, feline, bat, rat, monkey
製造商/商標名
Chemicon®
技術
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
NCBI登錄號
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
cat ... Chat(751512)
human ... CHAT(1103)
mouse ... Chat(12647)
rat ... Chat(290567)
rhesus monkey ... Chat(709977)
一般說明
乙酰胆碱(ACh)是运动神经元、神经节前自主神经元、神经节后副交感神经元、各种大脑区域和一些新兴的神经元样干细胞的常见神经递质。Ach 的代谢相对简单,仅涉及两种酶:用于合成的胆碱乙酰基转移酶(ChAT)和用于降解的乙酰胆碱酯酶(AChE)。此外,乙酰胆碱在除神经传递以外的神经元中几乎没有功能,并且似乎是神经元特异性的。似乎只有胆碱能神经元具有大量的ChAT,使得抗胆碱乙酰基转移酶成为有用的特异性标志物。
特異性
与其他物种的反应性尚未通过IHC得到确认。
大脑和中枢神经紧张的系统中的胆碱能神经元。
應用
免疫沉淀:
先前批次的1:200稀释液可从大脑和胎盘中免疫沉淀68 kDa活性ChAT。还会在人类和其他哺乳动物的中枢神经紧张系统的某些胆碱能神经元中沉淀出与ChAT共表达(但缺乏ChAT活性)的27 kDa蛋白。
最佳的工作稀释度和方案必须由最终用户确定。
先前批次的1:200稀释液可从大脑和胎盘中免疫沉淀68 kDa活性ChAT。还会在人类和其他哺乳动物的中枢神经紧张系统的某些胆碱能神经元中沉淀出与ChAT共表达(但缺乏ChAT活性)的27 kDa蛋白。
最佳的工作稀释度和方案必须由最终用户确定。
抗胆碱乙酰基转移酶(ChAT)抗体是一种抗胆碱乙酰基转移酶(ChAT)的抗体,用于IH、IH(P)、IP & WB,产品引用超过70次。
品質
通过免疫组化(石蜡)对正常大脑皮层组织进行常规评估。
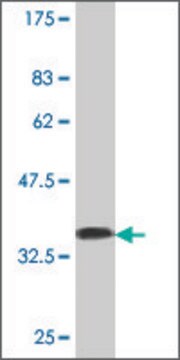
免疫组织化学(石蜡)分析:
正常大脑皮层ChAT(目录#AB143)染色。未经抗原修复处理的组织。使用带有HRP-DAB的IHC-Select Detection,将抗体稀释至1:100。 免疫反应性被视为神经元(棕色)的细胞体、树突和轴突上的染色模式。
免疫组织化学(石蜡)分析:
正常大脑皮层ChAT(目录#AB143)染色。未经抗原修复处理的组织。使用带有HRP-DAB的IHC-Select Detection,将抗体稀释至1:100。 免疫反应性被视为神经元(棕色)的细胞体、树突和轴突上的染色模式。
外觀
兔多克隆抗血清,液体,不含防腐剂。
分析報告
对照
大脑皮层组织。
大脑皮层组织。
其他說明
浓度:请参考批次特异性浓缩物的检验报告。
法律資訊
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
其他客户在看
K Sasaki et al.
Neuroscience, 92(4), 1287-1294 (1999-07-30)
We examined the effects of repeated subcutaneous injections of an acidic fibroblast growth factor fragment analog, [Ala16] acidic fibroblast growth factor (1-29), on learning and memory and on the choline acetyltransferase immunoreactivity of forebrain neurons in senescence-accelerated mice. One group
B M Kramer et al.
Neuroscience, 94(4), 1163-1172 (2000-01-07)
The role of the p75 nerve growth factor receptor in the retrograde transport of neurotrophins in the adult CNS was investigated by comparing the transport of 125I-labeled neurotrophins by normal and p75 nerve growth factor receptor-deficient cholinergic septohippocampal neurons. In
U Greferath et al.
Neuroscience, 100(2), 363-373 (2000-09-29)
We investigated age-related changes in the number and size of neurons positive for the p75 neurotrophin receptor in the cholinergic basal forebrain of female Dark Agouti rats. Since the integrity of these neurons is known to be closely associated with
E Jolkkonen et al.
Neuroscience, 111(1), 133-149 (2002-04-17)
The amygdaloid complex has a key role in the modulation of behavioral responses in life-threatening situations, including the direction of attentional responses to sensory stimuli. The pathways from the amygdala to the basal forebrain cholinergic system, which projects to the
C E E M van der Zee et al.
Neuroscience, 110(4), 641-651 (2002-04-06)
The p75 low-affinity neurotrophin receptor (p75(LNTR)) appears to have various functions that include enhancing nerve growth factor (NGF)-mediated survival by increasing TrkA (high-affinity NGF receptor) efficiency, and mediating apoptosis by acting as a ligand-regulated pro-apoptotic receptor. Here, we investigated the
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门