371962
H-89, Dihydrochloride
InSolution 10 mM, ≥99%, reversible ATP-competitive inhibitor of protein kinase A
别名:
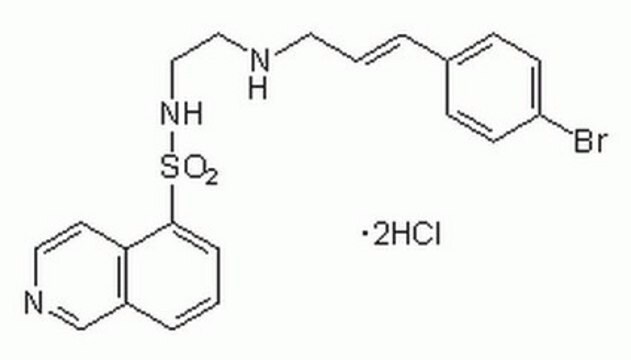
InSolution H-89, Dihydrochloride, N-[2-(( p-Bromocinnamyl)amino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide, 2HCl, PKA Inhibitor III, N-[2-((p-Bromocinnamyl)amino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide, 2HCl, PKA Inhibitor III
登录查看公司和协议定价
所有图片(1)
About This Item
经验公式(希尔记法):
C20H20BrN3O2S
分子量:
446.36
分類程式碼代碼:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.77
推荐产品
品質等級
化驗
≥99% (HPLC)
形狀
liquid
製造商/商標名
Calbiochem®
儲存條件
OK to freeze
protect from light
運輸包裝
wet ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
一般說明
A solution of H-89, Dihydrochloride (Cat. No. 371963) in anhydrous DMSO. H-89 is a cell-permeable selective and potent inhibitor of protein kinase A (Ki = 48 nM). Inhibits other kinases at several fold higher concentrations: myosin light chain kinase (Ki = 28.3 µM), Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (Ki = 29.7 µM), protein kinase C (Ki = 31.7 µM), casein kinase I (Ki = 38.3 µM), and Rho Kinase II (IC50 = 270 nM). May be used to discriminate between the effects of PKA and cAMP-regulated guanine-nucleotide-exchange factors (GEFs), such as GEFI or Epac (exchange protein directly activated by cAMP) and GEFII. Reported to induce neurite formation in NG 108-15 cells (~1 µM) by blocking the action of Rho kinase II.
生化/生理作用
Cell permeable: no
Primary Target
PKA
PKA
Product does not compete with ATP.
Reversible: no
Target Ki: 48 nM against protein kinase A
包裝
Packaged under inert gas
警告
Toxicity: Irritant (B)
外觀
A 10 mM (1 mg/193 µl) solution of H-89, 2HCl (Cat. No. 371963) in DMSO.
重構
Following initial thaw, aliquot and freeze (-20°C).
其他說明
Leemhuis, J., et al. 2002. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.300, 1000.
Davies, S.P. et al. 2000. Biochem. J.351, 95.
de Rooij, J., et al. 1998. Nature.396, 474.
Kawasaki, H., et al. 1998. Science.282, 2275.
Findik, D., et al. 1995. J. Cell. Biochem.57, 12.
Hidaka, H., and Kobayashi, R. 1992. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol.32, 377.
Geilen, C.C., et al. 1992. FEBS Lett.309, 381.
Chijiwa, T., et al. 1990. J. Biol. Chem.265, 5267.
Combest, W.L., et al. 1988. J. Neurochem.51, 1581.
Davies, S.P. et al. 2000. Biochem. J.351, 95.
de Rooij, J., et al. 1998. Nature.396, 474.
Kawasaki, H., et al. 1998. Science.282, 2275.
Findik, D., et al. 1995. J. Cell. Biochem.57, 12.
Hidaka, H., and Kobayashi, R. 1992. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol.32, 377.
Geilen, C.C., et al. 1992. FEBS Lett.309, 381.
Chijiwa, T., et al. 1990. J. Biol. Chem.265, 5267.
Combest, W.L., et al. 1988. J. Neurochem.51, 1581.
法律資訊
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
188.6 °F - closed cup - (Dimethylsulfoxide)
閃點(°C)
87 °C - closed cup - (Dimethylsulfoxide)
Nicole Welch et al.
iScience, 25(11), 105325-105325 (2022-11-09)
Skeletal muscle generation of ammonia, an endogenous cytotoxin, is increased during exercise. Perturbations in ammonia metabolism consistently occur in chronic diseases, and may blunt beneficial skeletal muscle molecular responses and protein homeostasis with exercise. Phosphorylation of skeletal muscle proteins mediates
Yanyong Xu et al.
Nature metabolism, 3(1), 59-74 (2021-01-20)
Activating transcription factor (ATF)3 is known to have an anti-inflammatory function, yet the role of hepatic ATF3 in lipoprotein metabolism or atherosclerosis remains unknown. Here we show that overexpression of human ATF3 in hepatocytes reduces the development of atherosclerosis in
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门