07-1016
抗-磷酸化-Upf1(Ser1127)抗体
from rabbit, purified by affinity chromatography
别名:
Regulator of nonsense transcripts 1, ATP-dependent helicase RENT1, Nonsense mRNA reducing factor 1, NORF1, Up-frameshift suppressor 1 homolog, hUpf1
登录查看公司和协议定价
所有图片(4)
About This Item
分類程式碼代碼:
12352203
eCl@ss:
32160702
NACRES:
NA.41
推荐产品
生物源
rabbit
品質等級
抗體表格
affinity isolated antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
純化經由
affinity chromatography
物種活性
mouse, human
物種活性(以同源性預測)
chicken (based on 100% sequence homology), zebrafish (based on 100% sequence homology), yeast (based on 100% sequence homology), bovine (based on 100% sequence homology), rat (based on 100% sequence homology)
技術
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
NCBI登錄號
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
wet ice
目標翻譯後修改
phosphorylation (pSer1127)
基因資訊
human ... UPF1(5976)
一般說明
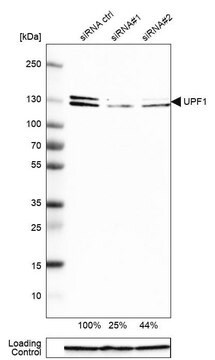
无义转录本1的调节剂(UniProt:Q92900;又称ATP依赖性解旋酶RENT1,无义mRNA还原因子1,NORF1,上移码抑制因子1同源物,hUpf1)由人UPF1(又称KIAA0221,RENT1)基因(基因ID:5976)编码。Upf1是Dna2/Nam7解旋酶家族的成员。它是含有过早终止密码子的mRNA的无义介导的衰变(NMD)所需的RNA依赖性解旋酶和ATPase。它在翻译终止后被募集到mRNA,并经历磷酸化和去磷酸化的循环。它被SMG1磷酸化,磷酸化被认为是NMD中必不可少的步骤,是形成mRNA监视复合物所必需的。磷酸化的Upf1被Est1b/SMG5,SMG6和SMG7识别,它们提供了与涉及核酸外切和核酸内切途径的mRNA降解机制的联系。超磷酸化形式靶向P体,而未磷酸化的蛋白质分布在整个细胞质中。Upf1的ATPase活性是分解经历NMD的mRNP所必需的,并且对于胚胎生存能力也是必不可少的。据报道,通过选择性剪接产生了Upf1的两种亚型。Upf1包含Upf1型锌指结构域(aa 121-272)和核苷酸结合结构域(aa 506-510)。
特異性
该兔多克隆抗体可检测多种物种中无义转录本1(RENT1)的调节剂。它靶向磷酸化Ser1127周围9个氨基酸内的表位。
免疫原
对应于Ser1127磷酸化的Upf1的KLH偶联线性肽。
表位:磷酸化Ser1127
應用
抗磷酸化UPF1(Ser1127)(目录号07-1016)是一种高度特异性的兔多克隆抗体,其靶向在Ser1127处磷酸化的无义转录物1(RENT1)的调节剂,并已在免疫沉淀,肽抑制测定和蛋白质印迹中进行了测试。
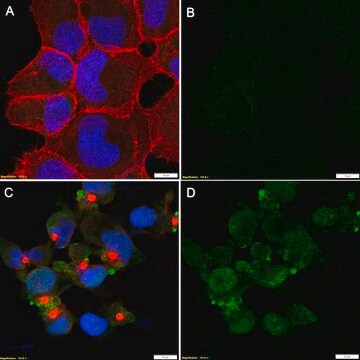
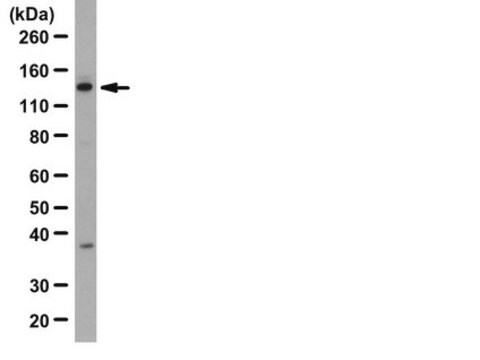
蛋白印迹分析: 来自代表性批次的1:1000稀释液在10 µg用Calyculin A和冈田酸处理的A431中检测到磷酸化Upf1 (Ser1127)。
肽抑制分析:来自代表性批次的1:1,000稀释液可阻断Calyculin A和冈田酸处理的NIH3T3中的磷酸化-Upf1(Ser1127)。
免疫沉淀分析:5 µg来自代表性批次的产品在用Calyculin a和冈田酸处理的NIH3T3中免疫沉淀磷酸化-UPF1(Ser1127)。
肽抑制分析:来自代表性批次的1:1,000稀释液可阻断Calyculin A和冈田酸处理的NIH3T3中的磷酸化-Upf1(Ser1127)。
免疫沉淀分析:5 µg来自代表性批次的产品在用Calyculin a和冈田酸处理的NIH3T3中免疫沉淀磷酸化-UPF1(Ser1127)。
品質
已通过蛋白质印迹在Calyculin A和冈田酸处理的NIH3T3中进行了评估。
蛋白质印迹分析:该抗体的1:1000稀释液在用Calyculin A(50 nM)和冈田酸(500 nM)处理30分钟的NIH3T3的10 µg裂解液中检测到磷酸化UPF1(Ser1127)。
蛋白质印迹分析:该抗体的1:1000稀释液在用Calyculin A(50 nM)和冈田酸(500 nM)处理30分钟的NIH3T3的10 µg裂解液中检测到磷酸化UPF1(Ser1127)。
標靶描述
观测值〜140 kDa。计算值为125 kDa。
其他說明
浓度:请参考批次特异性浓缩物的分析证书。
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Yang Zhao et al.
Nature communications, 11(1), 3345-3345 (2020-07-06)
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is an evolutionarily conserved RNA decay mechanism that has emerged as a potent cell-intrinsic restriction mechanism of retroviruses and positive-strand RNA viruses. However, whether NMD is capable of restricting DNA viruses is not known. The DNA
Feng Wang et al.
Nature communications, 14(1), 4760-4760 (2023-08-09)
Long-read RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) is a powerful technology for transcriptome analysis, but the relatively low throughput of current long-read sequencing platforms limits transcript coverage. One strategy for overcoming this bottleneck is targeted long-read RNA-seq for preselected gene panels. We present
Tatsuaki Kurosaki et al.
Genome biology, 22(1), 317-317 (2021-11-18)
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is an intellectual disability attributable to loss of fragile X protein (FMRP). We previously demonstrated that FMRP binds mRNAs targeted for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) and that FMRP loss results in hyperactivated NMD and inhibition of
Hanae Sato et al.
Nature communications, 12(1), 7203-7203 (2021-12-12)
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is an mRNA degradation pathway that eliminates transcripts containing premature termination codons (PTCs). Half-lives of the mRNAs containing PTCs demonstrate that a small percent escape surveillance and do not degrade. It is not known whether this
Sébastien Durand et al.
Nature communications, 7, 12434-12434 (2016-08-12)
Many gene expression factors contain repetitive phosphorylation sites for single kinases, but the functional significance is poorly understood. Here we present evidence for hyperphosphorylation as a mechanism allowing UPF1, the central factor in nonsense-mediated decay (NMD), to increasingly attract downstream
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门