推荐产品
等級
battery grade
品質等級
形狀
solution
環保替代產品特色
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
濃度
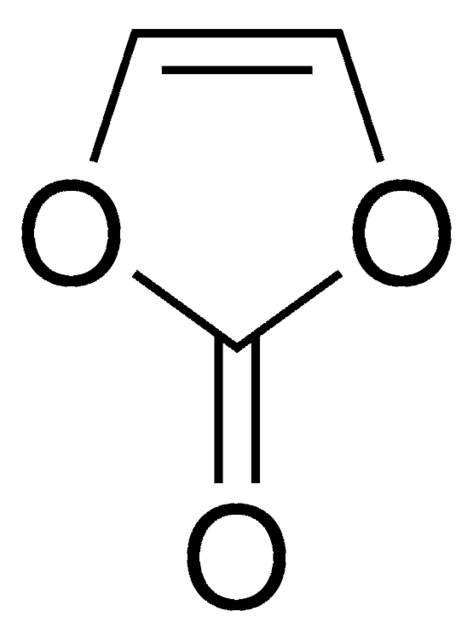
(1.0 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC)
雜質
<15 ppm H2O
<50 ppm HF
顏色
APHA: <50
bp
100 °C
密度
1.27 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
負離子痕跡
chloride (Cl-): ≤1 ppm
sulfate (SO42-): ≤2 ppm
正離子痕跡
Ca: ≤1 ppm
Fe: ≤1 ppm
K: ≤1 ppm
Na: ≤1 ppm
Pb: ≤1 ppm
應用
battery manufacturing
環保替代類別
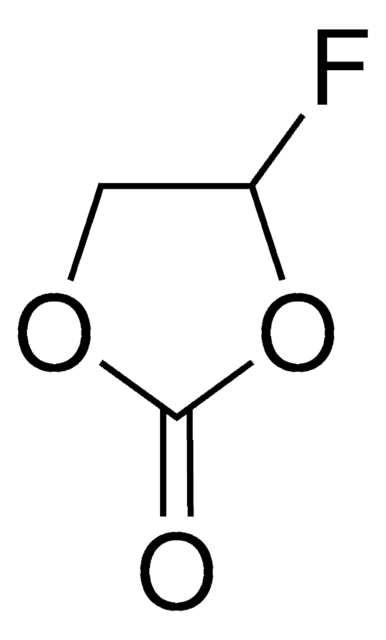
SMILES 字串
F[P-](F)(F)(F)(F)F.[Li+]
InChI
1S/F6P.Li/c1-7(2,3,4,5)6;/q-1;+1
InChI 密鑰
AXPLOJNSKRXQPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
相关类别
一般說明
應用
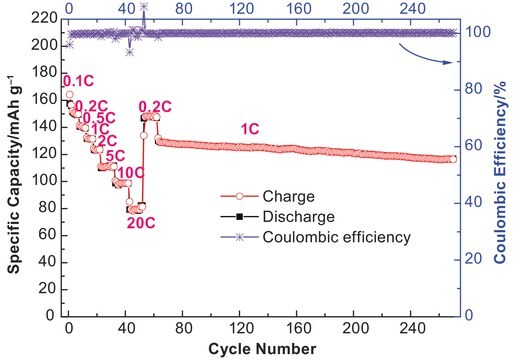
即用型电解质溶液有不同的溶剂混合物可供选择,可支持多种锂离子电池应用。这些溶液具有高纯度和电池级,因此也适合作为 LIB 研究的标准品。可通过混合电解质溶液或混合适当的添加剂来制备定制制剂。
其他說明
- 请勿与玻璃设备配合使用
- 所有工作都应在干燥空气下快速完成,以防止电解质的吸水和溶剂蒸发。
法律資訊
相關產品
訊號詞
Danger
危險分類
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Skin Corr. 1A - STOT RE 1 Inhalation - STOT RE 2 Oral
標靶器官
Bone,Teeth, Kidney
儲存類別代碼
3 - Flammable liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 2
閃點(°F)
86.0 °F
閃點(°C)
30 °C
其他客户在看
商品
Dr. Sun reviews the recent advances in solid-state rechargeable batteries and cover the fundamentals of solid electrolytes in solid-state batteries, the theory of ion conduction, and the structures and electrochemical processes of solid-state Li batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have been widely adopted as the most promising portable energy source in electronic devices because of their high working voltage, high energy density, and good cyclic performance.
The critical technical challenges associated with the commercialization of electric vehicle batteries include cost, performance, abuse tolerance, and lifespan.
Due to the adverse impact of the continued use of fossil fuels on the earth’s environment and climate, researchers have been asked to develop new approaches for producing power using renewable sources like wind and solar energy
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门