SML2140
TCS 401
≥98% (HPLC)
Sinónimos:
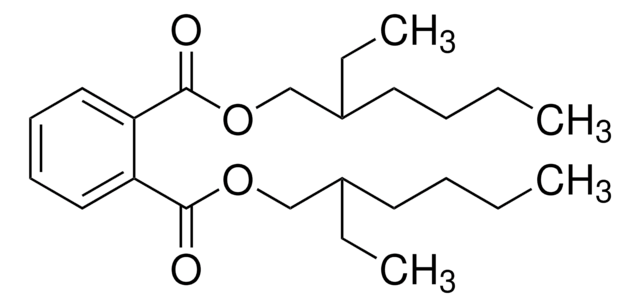
2-[(Carboxycarbonyl)amino]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[2,3-c]pyridine-3-carboxylic acid hydrochloride, TCS-401, TCS401
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Fórmula empírica (notación de Hill):
C10H10N2O5S · xHCl
Número de CAS:
Peso molecular:
270.26 (free base basis)
Código UNSPSC:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.77
Productos recomendados
Análisis
≥98% (HPLC)
formulario
powder
color
white to beige
solubilidad
0.1 M NaOH: 2 mg/mL, clear (warmed)
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
TCS 401 is a selective inhibitor of protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B), which plays a key role in the negative regulation of the insulin signaling pathway, contributing to insulin resistance. It exhibited Ki values of 290 nM for PTP1B, with greater than 100-fold or more selectivity compared to other phosphatases. Inhibition of PTP1B by TCS 401 has been shown to sensitize the insulin signaling pathway and increase dopamine release in response to insulin. TCS-401 has also been shown to promote endothelial cell motility and to induce differentiation of retinal pigment epithelial cells toward improved contractility and motility.
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Steve C Fordahl et al.
ACS chemical neuroscience, 8(2), 290-299 (2016-12-15)
Systemically released insulin crosses the blood-brain barrier and binds to insulin receptors on several neural cell types, including dopaminergic neurons. Insulin has been shown to decrease dopamine neuron firing in the ventral tegmental area (VTA), but potentiate release and reuptake
L F Iversen et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 275(14), 10300-10307 (2000-04-01)
Several protein-tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) have been proposed to act as negative regulators of insulin signaling. Recent studies have shown increased insulin sensitivity and resistance to obesity in PTP1B knockout mice, thus pointing to this enzyme as a potential drug target
Samuel Legeay et al.
Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie, 127, 110200-110200 (2020-05-18)
Diabetes notably increases the risk for endothelial dysfunction, a main precursor for microvascular complications. While endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) have been associated with endothelial dysfunction in resistance vessels, whether these mechanisms also contribute to
Zhao-dong Du et al.
Molecular vision, 21, 523-531 (2015-05-23)
To determine whether protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) is expressed in rat retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells, to evaluate whether inhibition of PTP1B contributes to initiation of RPE cells into an active state, and to investigate the signaling pathways involved
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico