M7659
Myosin Heavy Chain from rabbit muscle
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
Sinónimos:
ATPase inactive whole chain myosin
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
rabbit muscle
Nivel de calidad
formulario
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
técnicas
electrophoresis: suitable
Nº de acceso UniProt
actividad extraña
ATPase Activity ≤0.01 units/mg protein
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
Información sobre el gen
rabbit ... PBV1SPCR2(100009284)
Descripción general
Aplicación
- in SDS analysis of myosin heavy chain (MHC) composition and content
- for microinjection into the outflow of heart (blood serum) and the cephalic cavities (embryonic cerebrospinal fluid) of chick embryo
- as a muscle protein, to study the role of ascorbate as a facilitator of glycogen storage in muscles
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Forma física
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
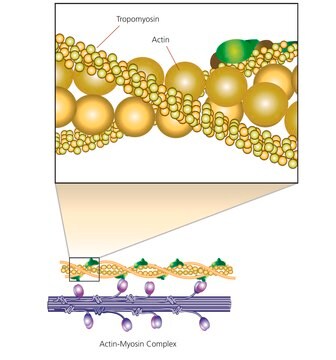
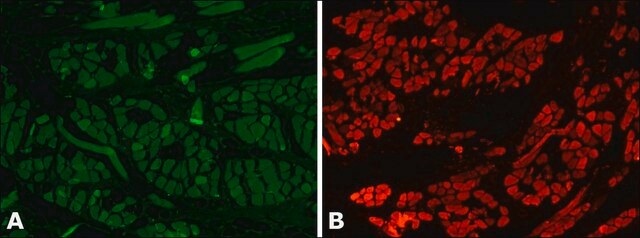
Myosins are a family of ATP-dependent motor proteins. Myosin II is the major contractile protein involved in eukaryotic muscle contraction by “walking” along actin microfilaments of the sarcomere
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico