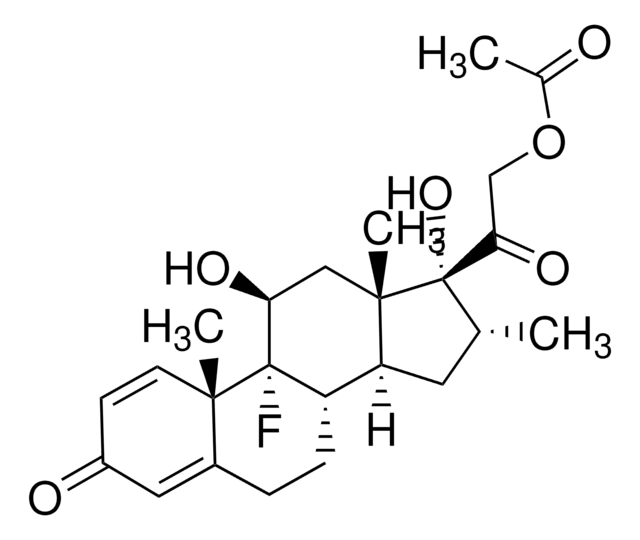
D9184
Dexametasona
meets USP testing specifications
Sinónimos:
(11β,16α)-9-Fluoro-11,17,21-trihidroxi-16-metilpregna-1,4-dieno-3,20-diona, 9α-Fluoro-16α-metil-11β,17α,21-trihidroxi-1,4-pregnadieno-3,20-diona, 9α-fluoro-16α-metilprednisolona, Prednisolona F
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
synthetic (organic)
Nivel de calidad
Agency
USP/NF
meets USP testing specifications
Ensayo
97.0-102.0%
Formulario
solid
mp
262-264 °C (lit.)
Condiciones de envío
ambient
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
cadena SMILES
C[C@@H]1C[C@H]2[C@@H]3CCC4=CC(=O)C=C[C@]4(C)[C@@]3(F)[C@@H](O)C[C@]2(C)[C@@]1(O)C(=O)CO
InChI
1S/C22H29FO5/c1-12-8-16-15-5-4-13-9-14(25)6-7-19(13,2)21(15,23)17(26)10-20(16,3)22(12,28)18(27)11-24/h6-7,9,12,15-17,24,26,28H,4-5,8,10-11H2,1-3H3/t12-,15+,16+,17+,19+,20+,21+,22+/m1/s1
Clave InChI
UREBDLICKHMUKA-CXSFZGCWSA-N
Información sobre el gen
human ... ABCB1(5243) , CYP3A4(1576) , IL4(3565) , IL5(3567) , NR3C1(2908)
mouse ... Abcb1a(18671) , Abcb1b(18669) , Ifng(15978) , Nos2(18126) , Ptgs2(19225) , Tnf(21926)
rat ... Ar(24208) , Nr3c1(24413) , Tnf(24835)
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Descripción general
Aplicación
- To investigate the osteogenic differentiation and chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).
- In α-MEM (minimum essential medium) for inducing the osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow and umbilical cord blood.
- For the isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from 6- to 8-week-old C57BL/6J mice.
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Palabra de señalización
Danger
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Repr. 1B
Código de clase de almacenamiento
6.1C - Combustible, acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico