189825
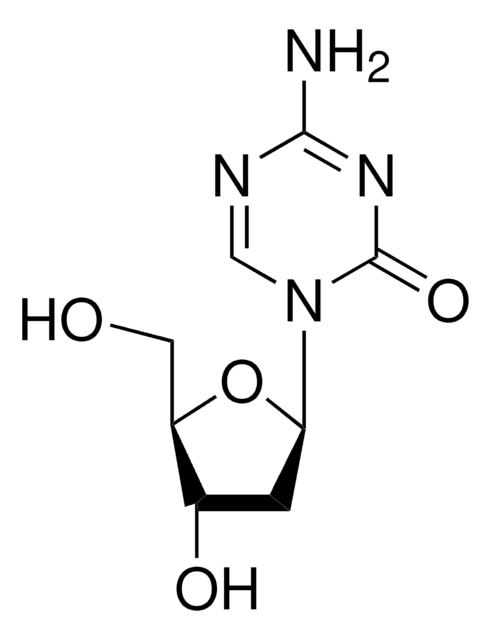
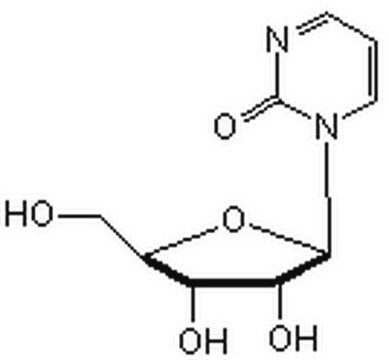
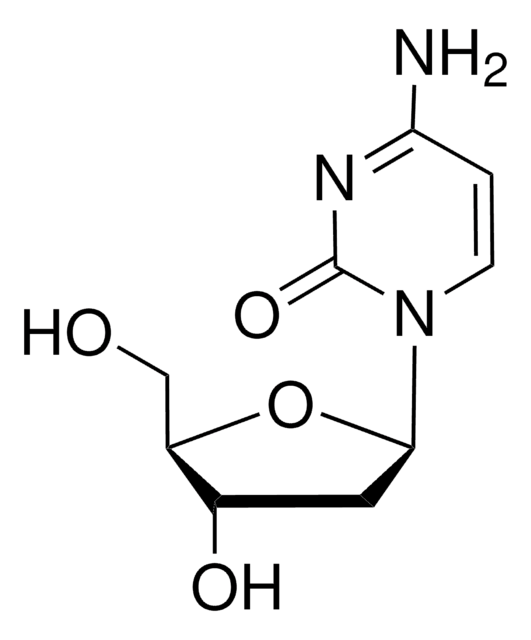
5-Aza-2′-Deoxycytidine
A cytosine analog that acts as a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor.
Sinónimos:
5-Aza-2′-Deoxycytidine, 5-Aza-CdR, 5-Aza-dC, 2′-Deoxy-5-azacytidine, Decitabine
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Nivel de calidad
Análisis
≥98% (HPLC)
formulario
lyophilized
fabricante / nombre comercial
Calbiochem®
condiciones de almacenamiento
OK to freeze
solubilidad
methanol: 1 mg/mL
50% acetic acid: 25 mg/mL
DMSO: 25 mg/mL
Condiciones de envío
ambient
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
InChI
1S/C8H12N4O4/c9-7-10-3-12(8(15)11-7)6-1-4(14)5(2-13)16-6/h3-6,13-14H,1-2H2,(H2,9,11,15)
Clave InChI
XAUDJQYHKZQPEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Descripción general
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
DNA methyltransferase inhibitor
Envase
Advertencia
Nota de preparación
Reconstitución
Otras notas
Takebayashi, S., et al. 2001. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.288, 921.
Zhu, W.G., et al. 2001. Cancer Res.61, 1327.
Hopkins-Donaldson, S., et al. 2000. Cancer Res.60, 4315.
Haaf, T. 1995. Pharmacol. Ther.65, 19.
Jones, P.A., and Taylor, S.M. 1980. Cell20, 85.
Información legal
Palabra de señalización
Danger
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Muta. 2 - Repr. 1B - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Órganos de actuación
Respiratory system
Código de clase de almacenamiento
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico