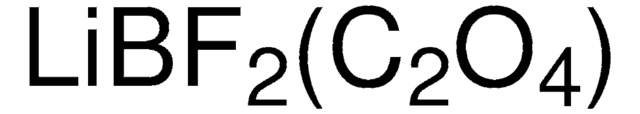757136
Lithium bis(oxalato)borate
Sinónimos:
LiBOB, Lithium bis(ethanedioato)borate, Lithium bis(oxalate)borate
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Formulario
powder or crystals
Nivel de calidad
características de los productos alternativos más sostenibles
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
mp
>300 °C (lit.)
aplicaciones
battery manufacturing
categoría alternativa más sostenible
cadena SMILES
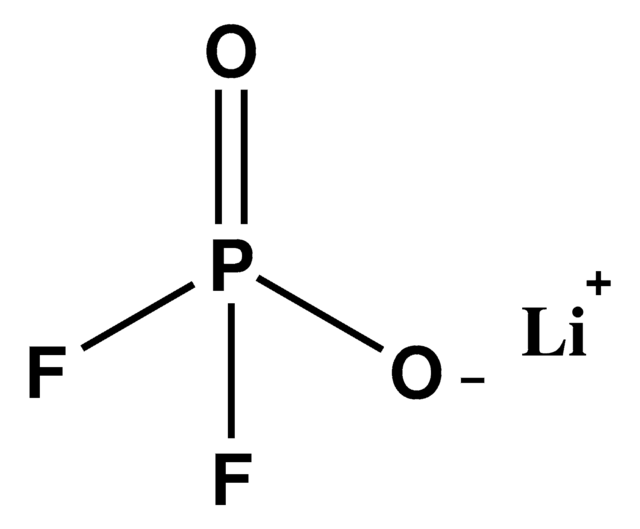
[Li+].O=C1O[B-]2(OC1=O)OC(=O)C(=O)O2
InChI
1S/C4BO8.Li/c6-1-2(7)11-5(10-1)12-3(8)4(9)13-5;/q-1;+1
Clave InChI
NVQAYVUCVASGDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Descripción general
Aplicación
Información legal
Producto relacionado
Palabra de señalización
Danger
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Sens. 1A
Código de clase de almacenamiento
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 1
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
Dr. Sun reviews the recent advances in solid-state rechargeable batteries and cover the fundamentals of solid electrolytes in solid-state batteries, the theory of ion conduction, and the structures and electrochemical processes of solid-state Li batteries.
Li-ion batteries are currently the focus of numerous research efforts with applications designed to reduce carbon-based emissions and improve energy storage capabilities.
The critical technical challenges associated with the commercialization of electric vehicle batteries include cost, performance, abuse tolerance, and lifespan.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have been widely adopted as the most promising portable energy source in electronic devices because of their high working voltage, high energy density, and good cyclic performance.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico