H4916
BMP4, human
HumanKine®, recombinant, Xeno-free, >95% (SDS-PAGE), suitable for cell culture
Synonym(e):
BMP-4
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
product name
Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4 human, BMP-4, recombinant, expressed in HEK 293 cells, HumanKine®, suitable for cell culture
Biologische Quelle
human
Qualitätsniveau
Rekombinant
expressed in HEK 293 cells
Assay
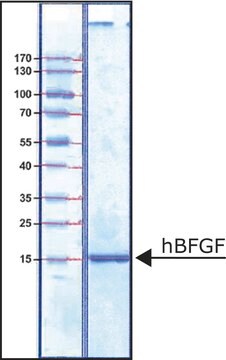
>95% (SDS-PAGE)
Form
lyophilized powder
Wirksamkeit
≤10 ng/mL EC50
Qualität
endotoxin tested
Mol-Gew.
dimer 34 kDa (glycosylated)
Verpackung
pkg of 10 μg
pkg of 100 μg
pkg of 1000 μg
Lagerbedingungen
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
Methode(n)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
Verunreinigungen
<1 EU/μg Endotoxin level
UniProt-Hinterlegungsnummer
Lagertemp.
−20°C
Angaben zum Gen
human ... BMP4(652)
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
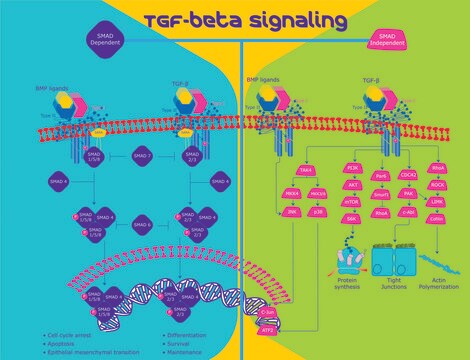
Cellular responses to BMP-4 are mediated by the formation of hetero-oligomeric complexes of type I and type II serine/threonine kinase receptors, which play significant roles in BMP binding and signaling. Two BMP type I receptors and one BMP type II receptor have been identified. Both BMP type I receptors bind BMP-4 with high-affinity in the absence of BMP receptor type II.
Physikalische Form
Angaben zur Herstellung
Hinweis zur Analyse
Rechtliche Hinweise
Inhibitor
Vergleichbares Produkt
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.