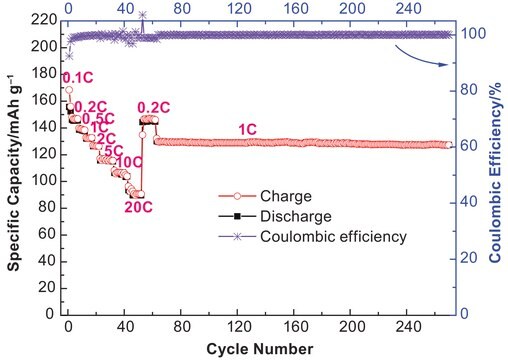
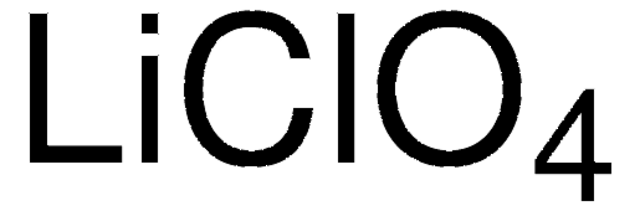746789
Lithiumhexafluorophosphat -Lösung
in propylene carbonate, 1.0 M LiPF6 in PC, battery grade
Synonym(e):
1.0 M LiPF6 PC
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualität
battery grade
Qualitätsniveau
Form
solution
Grünere Alternativprodukt-Eigenschaften
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Konzentration
(1.0 M LiPF6 in PC)
Verunreinigungen
<15 ppm H2O
<50 ppm HF
Farbe
APHA: <50
bp
>200 °C
Dichte
1.31 g/mL at 25 °C
Anionenspuren
chloride (Cl-): ≤1 ppm
sulfate (SO42-): ≤2 ppm
Kationenspuren
Ca: ≤1 ppm
Fe: ≤1 ppm
K: ≤1 ppm
Na: ≤1 ppm
Pb: ≤1 ppm
Anwendung(en)
battery manufacturing
Grünere Alternativprodukt-Kategorie
, Enabling
SMILES String
F[P-](F)(F)(F)(F)F.[Li+]
InChI
1S/F6P.Li/c1-7(2,3,4,5)6;/q-1;+1
InChIKey
AXPLOJNSKRXQPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
The ready-to-use electrolyte solutions are available in different solvent blends and can support a wide variety of lithium ion battery applications. These solutions are high purity and battery grade thus making them also suitable as standards in LIB research. Customized formulations can be made by inter-mixing the electrolyte solutions or by mixing appropriate of additives.
Sonstige Hinweise
- Do not use with glass equipment
- All work should be done very quickly under dry air to prevent electrolytes from water uptake and solvent vaporization.
Rechtliche Hinweise
Ähnliches Produkt
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT RE 1 Inhalation
Zielorgane
Bone,Teeth
Lagerklassenschlüssel
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 2
Flammpunkt (°F)
266.0 °F
Flammpunkt (°C)
130 °C
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Dr. Sun reviews the recent advances in solid-state rechargeable batteries and cover the fundamentals of solid electrolytes in solid-state batteries, the theory of ion conduction, and the structures and electrochemical processes of solid-state Li batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have been widely adopted as the most promising portable energy source in electronic devices because of their high working voltage, high energy density, and good cyclic performance.
Li-ion batteries are currently the focus of numerous research efforts with applications designed to reduce carbon-based emissions and improve energy storage capabilities.
The critical technical challenges associated with the commercialization of electric vehicle batteries include cost, performance, abuse tolerance, and lifespan.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.