Wichtige Dokumente
310328
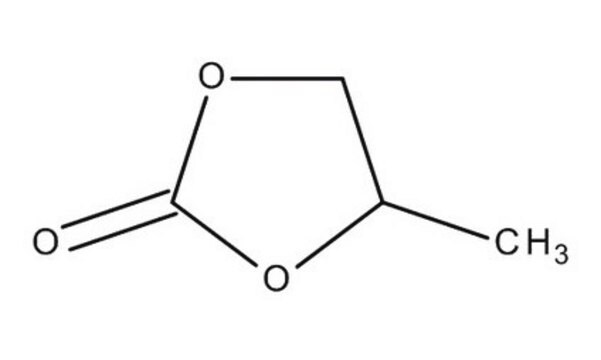
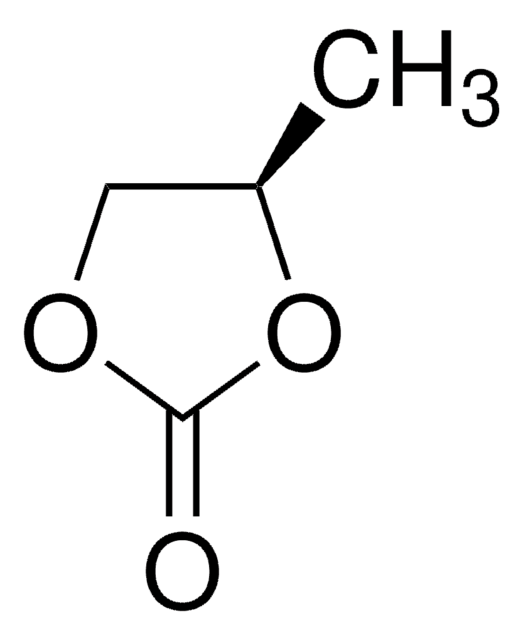
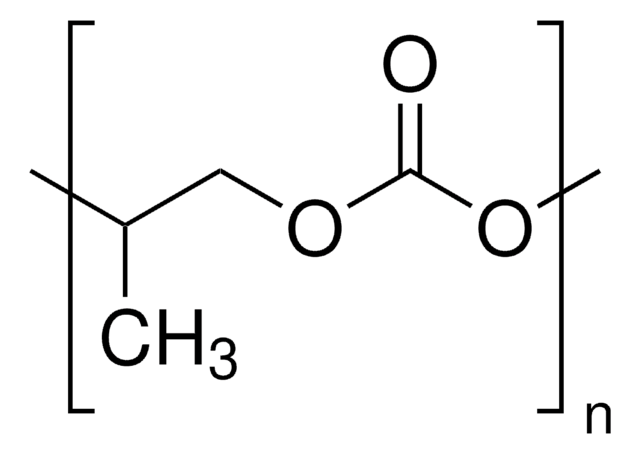
Propylencarbonat
anhydrous, 99.7%
Synonym(e):
1,2-Propandiol, zyklisches Carbonat, 4-Methyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-one
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualität
anhydrous
Qualitätsniveau
Dampfdruck
0.13 mmHg ( 20 °C)
0.98 mmHg ( 50 °C)
Assay
99.7%
Form
liquid
Selbstzündungstemp.
851 °F
Expl.-Gr.
14.3 %
Verunreinigungen
<0.002% water
<0.005% water (100 mL pkg)
Brechungsindex
n20/D 1.421 (lit.)
pH-Wert
7 (20 °C, 200 g/L)
bp
240 °C (lit.)
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
−55 °C (lit.)
Dichte
1.204 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES String
CC1COC(=O)O1
InChI
1S/C4H6O3/c1-3-2-6-4(5)7-3/h3H,2H2,1H3
InChIKey
RUOJZAUFBMNUDX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Verwandte Kategorien
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Eye Irrit. 2
Lagerklassenschlüssel
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flammpunkt (°F)
269.6 °F - closed cup
Flammpunkt (°C)
132 °C - closed cup
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Research and development of solid-state lithium fast-ion conductors is crucial because they can be potentially used as solid electrolytes in all-solid-state batteries, which may solve the safety and energy-density related issues of conventional lithium-ion batteries that use liquid (farmable organic) electrolytes.
The critical technical challenges associated with the commercialization of electric vehicle batteries include cost, performance, abuse tolerance, and lifespan.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.