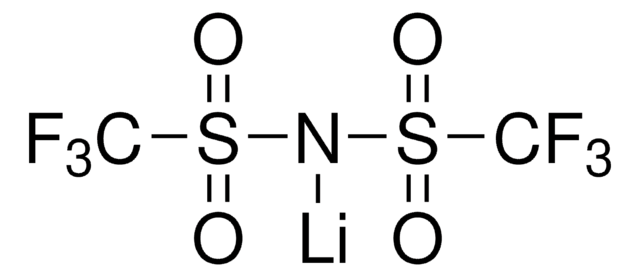
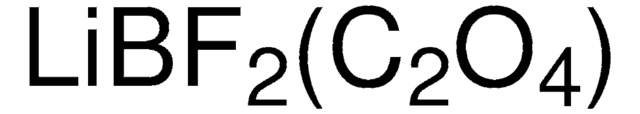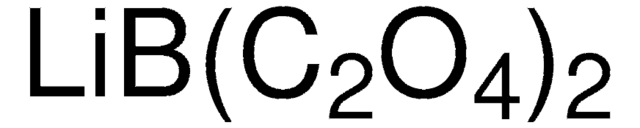450227
Lithiumhexafluorophosphat
battery grade, ≥99.99% trace metals basis
Synonym(e):
Lithiumphosphorfluorid
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualität
battery grade
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
≥99.99% trace metals basis
Form
powder
Grünere Alternativprodukt-Eigenschaften
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Verunreinigungen
≤100.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
200 °C (dec.) (lit.)
Anwendung(en)
battery manufacturing
Grünere Alternativprodukt-Kategorie
SMILES String
[Li+].F[P-](F)(F)(F)(F)F
InChI
1S/F6P.Li/c1-7(2,3,4,5)6;/q-1;+1
InChIKey
AXPLOJNSKRXQPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Sonstige Hinweise
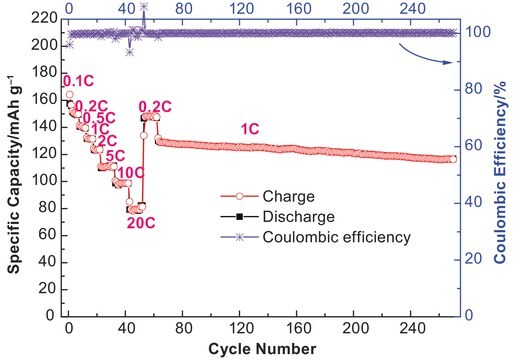
Herstellung und Charakterisierung von Lithium-Hexafluorophosphaten als Elektrolyte für Lithium-Ionen-Akkus.
Ähnliches Produkt
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Skin Corr. 1A - STOT RE 1 Inhalation
Zielorgane
Bone,Teeth
Lagerklassenschlüssel
6.1B - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 2
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Increasing fuel costs and concerns about greenhouse gas emissions have spurred the growth in sales of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) that carry a battery pack to supplement the performance of the internal combustion engine (ICE).
Dr. Sun reviews the recent advances in solid-state rechargeable batteries and cover the fundamentals of solid electrolytes in solid-state batteries, the theory of ion conduction, and the structures and electrochemical processes of solid-state Li batteries.
Research and development of solid-state lithium fast-ion conductors is crucial because they can be potentially used as solid electrolytes in all-solid-state batteries, which may solve the safety and energy-density related issues of conventional lithium-ion batteries that use liquid (farmable organic) electrolytes.
Discover more about advancements being made to improve energy density of lithium ion battery materials.
Verwandter Inhalt
Batteries, fuel cells, and supercapacitors rely on electrochemical energy production. Understand their operation and electron/ion transport separation.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.