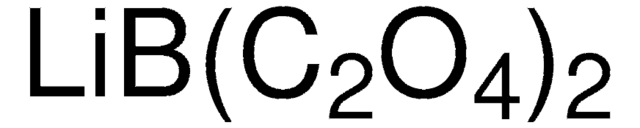Wichtige Dokumente
774138
Lithium difluoro(oxalato)borate
Synonym(e):
LIDFOB, LIF2OB, LIFOB, LIODFB, Lithium difluoro(ethanedioato)borate, Lithium oxalatodigluoroborate
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Form
powder
Qualitätsniveau
Grünere Alternativprodukt-Eigenschaften
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
265-271 °C
Anwendung(en)
battery manufacturing
Grünere Alternativprodukt-Kategorie
, Enabling
SMILES String
F[B-]1(OC(C(O1)=O)=O)F.[Li+]
InChI
1S/C2BF2O4.Li/c4-3(5)8-1(6)2(7)9-3;/q-1;+1
InChIKey
MEDDCIKGDMDORY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Leistungsmerkmale und Vorteile
✔ Increases battery life
✔ Stabilizes SEI layer
✔ Suitable for fast charging and low temperatures
Ähnliches Produkt
Signalwort
Warning
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Zielorgane
Respiratory system
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Dr. Sun reviews the recent advances in solid-state rechargeable batteries and cover the fundamentals of solid electrolytes in solid-state batteries, the theory of ion conduction, and the structures and electrochemical processes of solid-state Li batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have been widely adopted as the most promising portable energy source in electronic devices because of their high working voltage, high energy density, and good cyclic performance.
Li-ion batteries are currently the focus of numerous research efforts with applications designed to reduce carbon-based emissions and improve energy storage capabilities.
The critical technical challenges associated with the commercialization of electric vehicle batteries include cost, performance, abuse tolerance, and lifespan.
Verwandter Inhalt
Batteries, fuel cells, and supercapacitors rely on electrochemical energy production. Understand their operation and electron/ion transport separation.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.