Wichtige Dokumente
39391
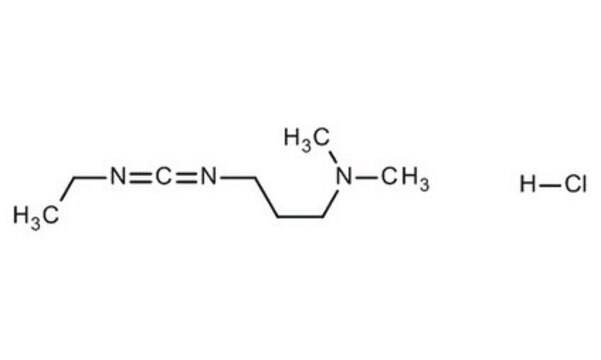
N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethyl-carbodiimid
≥97.0% (T), for peptide synthesis
Synonym(e):
N-Ethyl-N′-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimid, EDC, WSC
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Produktbezeichnung
N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethyl-carbodiimid, ≥97.0% (T)
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
≥97.0% (T)
Form
liquid
Eignung der Reaktion
reaction type: Coupling Reactions
Brechungsindex
n20/D 1.461
Dichte
0.877 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
Anwendung(en)
peptide synthesis
Funktionelle Gruppe
amine
Lagertemp.
−20°C
SMILES String
CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C
InChI
1S/C8H17N3/c1-4-9-8-10-6-5-7-11(2)3/h4-7H2,1-3H3
InChIKey
LMDZBCPBFSXMTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Signalwort
Danger
Gefahreneinstufungen
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1A - Skin Sens. 1A - STOT RE 2 Oral
Zielorgane
Stomach,large intestine,lymph node
Lagerklassenschlüssel
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Carbodiimide-mediated peptide coupling remains to the most frequently used technique.
Collagen molecules play a critical role in tissue architecture and strength, and in cell-matrix interactions as insoluble ligands to regulate the diverse phenotypic activities of cells.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.