T7E1001
T7 Endonuclease Detection Assay
Gene editing analysis kit with T7 endonuclease digestion and detection by SDS-PAGE
Sinonimo/i:
T7 endonuclease assay
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Codice UNSPSC:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.51
Prodotti consigliati
Confezionamento
kit of 6 vials (reagents for 25 Reactions)
Condizioni di spedizione
dry ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Descrizione generale
The T7 Endonuclease Detection Assay is a well-known method for detecting genome editing events from CRISPR, Zinc-finger nuclease, and TALEN gene targeting. Originally identified from Escherichia coli bacteriophage, the T7 endonuclease can cleave mismatched heteroduplex DNA, Holliday junctions, branched DNA, and cruciform DNA.
Following a gene editing experiment, genomic DNA surrounding the target locus is amplified by PCR, and the PCR amplicons are denatured and reannealed through heating and slow cooling. If NHEJ events have occurred, then, after reannealing, several products are possible. Homoduplexes can form where a WT strand is reannealead to a WT strand or an indel-carrying strand is reannealed to an indel-carrying strand. Heteroduplexes form when a WT strand is reannealed to an indel-carrying strand causing a mismatch. Heteroduplex products with mismatches are cleaved by the T7 endonuclease. Separating the DNA products after treatment with T7 endonuclease by gel electrophoresis will result in a banding pattern indicative of the amount of heteroduplexes in the sample. The amount of cleaved heteroduplexes is directly related to the amount of indel activity.
Following a gene editing experiment, genomic DNA surrounding the target locus is amplified by PCR, and the PCR amplicons are denatured and reannealed through heating and slow cooling. If NHEJ events have occurred, then, after reannealing, several products are possible. Homoduplexes can form where a WT strand is reannealead to a WT strand or an indel-carrying strand is reannealed to an indel-carrying strand. Heteroduplexes form when a WT strand is reannealed to an indel-carrying strand causing a mismatch. Heteroduplex products with mismatches are cleaved by the T7 endonuclease. Separating the DNA products after treatment with T7 endonuclease by gel electrophoresis will result in a banding pattern indicative of the amount of heteroduplexes in the sample. The amount of cleaved heteroduplexes is directly related to the amount of indel activity.
Applicazioni
Functional Genomics; Target Validation; Genome Editing
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
- Technically simple method based on well-known techniques
- Easily interpretable results
- Fast analysis turnaround
- Cost-effective
Componenti
Each kit consists of:
- one vial of T7 Endonuclease I
- one vial of Control Template and Primer Mix
- one vial of Buffer solution
- one vial of DNA Ladder - 1KB
- one vial of Gel Loading Dye (6X)
- one vial of Proteinase K
Principio
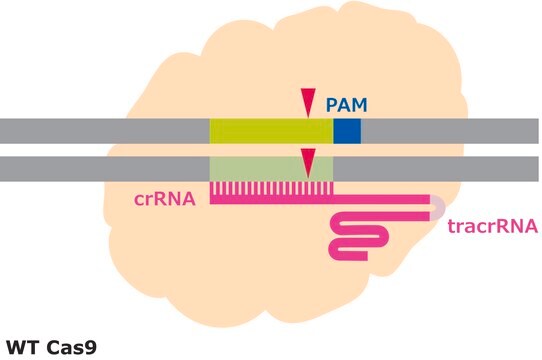
CRISPR/Cas systems are employed by bacteria and archaea as a defense against invading viruses and plasmids. Recently, the type II CRISPR/Cas system from the bacterium Streptococcus pyogenes has been engineered to function in eukaryotic systems using two molecular components: a single Cas9 protein and a non-coding guide RNA (gRNA). The Cas9 endonuclease can be programmed with a gRNA, directing a DNA double-strand break (DSB) at a desired genomic location. Similar to DSBs are also induced by Zinc-finger nucleases (ZFNs) and TALENs. The cell then activates endogenous DNA repair processes, either non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR), to heal the targeted DSB.
Efficiency in gene editing can vary in large part due to the target sequences. Chromatin structure and some sequence elements, for example high GC-content, can inhibit editing at some genomic sequences, affecting sgRNA activity. Additionally, favorable bases in the sgRNA sequence such as a guanine proximal to the PAM can promote sgRNA activity, but these preferred bases may not be available at the target site. It is important to evaluate the gene editing ability of several sgRNAs by quantifying the frequency of modifications using a method like T7 endonuclease mismatch detection.
Efficiency in gene editing can vary in large part due to the target sequences. Chromatin structure and some sequence elements, for example high GC-content, can inhibit editing at some genomic sequences, affecting sgRNA activity. Additionally, favorable bases in the sgRNA sequence such as a guanine proximal to the PAM can promote sgRNA activity, but these preferred bases may not be available at the target site. It is important to evaluate the gene editing ability of several sgRNAs by quantifying the frequency of modifications using a method like T7 endonuclease mismatch detection.
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Resp. Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documenti section.
Se ti serve aiuto, non esitare a contattarci Servizio Clienti
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.