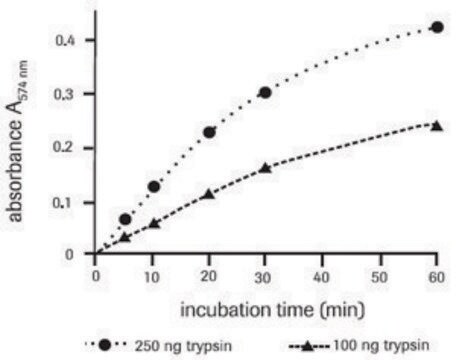
SRP2151
HCV-NS4A/NS3-1b Protease, Histag, strain HC-J4 from hepatitis C virus
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ≥80% (SDS-PAGE)
Sinonimo/i:
Hepatitis C virus NS3 protease, NS3, NS4ANS3 complex, pfam02907
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
hepatitis C virus
Ricombinante
expressed in E. coli
Saggio
≥80% (SDS-PAGE)
Stato
frozen liquid
PM
~22.7 kDa
Confezionamento
pkg of 10 μg
Concentrazione
500 μg/mL
Colore
colorless to clear
N° accesso NCBI
Condizioni di spedizione
dry ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−70°C
Informazioni sul gene
hepatitis C virus ... HCVgp1(951475)
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Stato fisico
Nota sulla preparazione
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Non trovi la versione di tuo interesse?
Se hai bisogno di una versione specifica, puoi cercare il certificato tramite il numero di lotto.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.