SBR00023
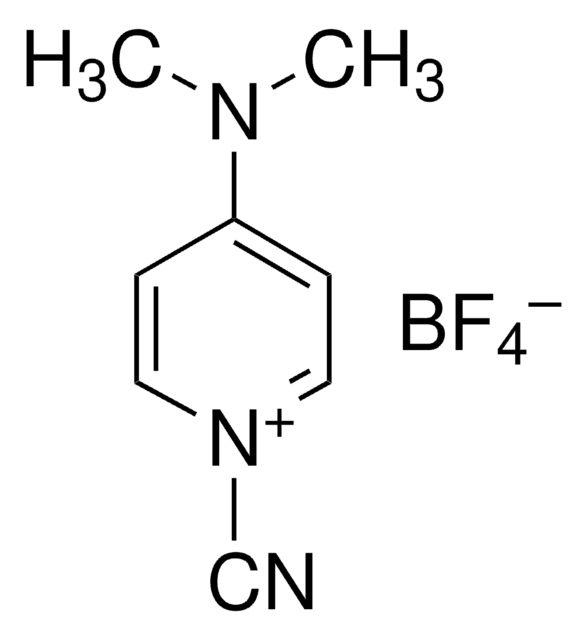
1-Cyano-4-dimethylaminopyridinium tetrafluoroborate Ready Made Solution
organic cyanylating reagent, 100 mg/mL in acetonitrile
Sinonimo/i:
4-(dimethylamino)pyridin-1-ium-1-carbonitrile tetrafluoroborate, CDAP
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
synthetic
Saggio
≥97%
Forma fisica
liquid
PM
234.99
Concentrazione
100 mg/mL in acetonitrile
Condizioni di spedizione
dry ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
InChI
1S/C8H10N3.BF4/c1-10(2)8-3-5-11(7-9)6-4-8;2-1(3,4)5/h3-6H,1-2H3;/q+1;-1
MBLVMDCQDCVKNE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
Azioni biochim/fisiol
CDAP is considered to be a less toxic reagent as compared to cyanogen bromide (CNBr) (a known polysaccharides activator). In addition, CDAP is easier to use as it can be employed at a lower pH and has fewer side reactions. It is known that CDAP polysaccharide activation efficiency is optimal at pH 9-10. It was also reported that direct conjugation of protein to CDAP-activated polysaccharides can be performed under mildly alkaline conditions (pH 7-9). It has also been reported that proteins could also be conjugated to CDAP-activated polysaccharides at pH 5.
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
- Readily available solution, that reduces the need for preparation time
- Versatile and adaptable for vaccine and biochemical research
Nota sulla preparazione
Altre note
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
3 - Flammable liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
35.6 °F
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
2 °C
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.