SAB5500113
Anti-Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Antibody
rabbit monoclonal, SP78
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Nome del prodotto
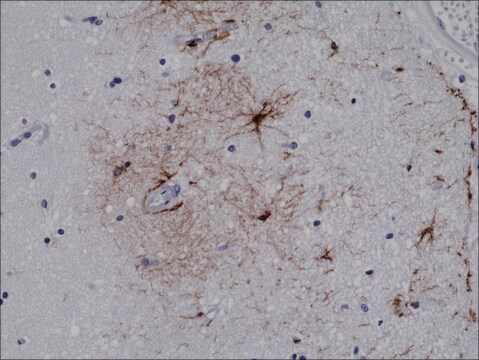
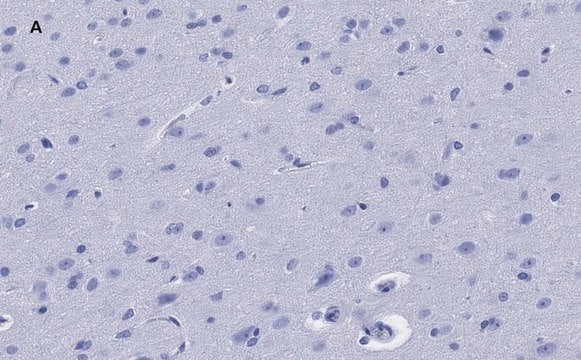
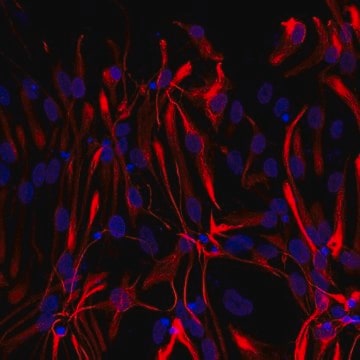
Anti-GFAP antibody, Rabbit monoclonal, recombinant, expressed in proprietary host, clone SP78, affinity isolated antibody
Origine biologica
rabbit
Livello qualitativo
Ricombinante
expressed in proprietary host
Coniugato
unconjugated
Forma dell’anticorpo
affinity isolated antibody
Tipo di anticorpo
primary antibodies
Clone
SP78, monoclonal
Reattività contro le specie
human (tested)
Reattività contro le specie (prevista in base all’omologia)
mouse, bovine, dog, rabbit, pig, rat
tecniche
immunohistochemistry: 1:100
Isotipo
IgG
N° accesso UniProt
Condizioni di spedizione
wet ice
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
modifica post-traduzionali bersaglio
unmodified
Informazioni sul gene
human ... GFAP(2670)
Descrizione generale
Immunogeno
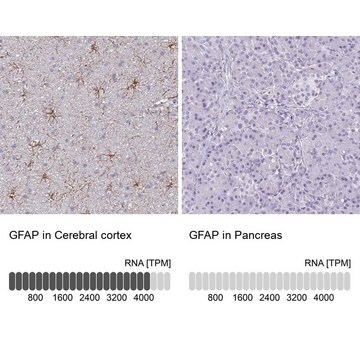
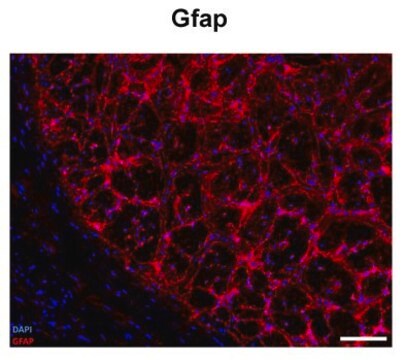
Applicazioni
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
Stato fisico
Esclusione di responsabilità
Non trovi il prodotto giusto?
Prova il nostro Motore di ricerca dei prodotti.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 2
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.