L4765
Lactoferrin from bovine colostrum
≥85% (SDS-PAGE)
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
bovine colostrum
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥85% (SDS-PAGE)
Stato
powder
PM
~90 kDa
tecniche
electrophoresis: suitable
ion chromatography: suitable
Impurezze
salt, essentially free
Solubilità
H2O: soluble 5 mg/mL
N° accesso UniProt
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Informazioni sul gene
cow ... LTF(280846)
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Lactoferrin from bovine colostrum corresponds to a molecular weight of 80 kDa. It is a glycosylated protein and belongs to the transferrin family. Bovine lactoferrin has N and C-terminal lobes homologous to human lactoferrin.
Applicazioni
Lactoferrin from bovine colostrum has been used as standard protein in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)- polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) for the quantification of IgG samples. It has also been used to test its effect in inducing autoimmune pancreatitis.
Lactoferrin from bovine colostrum was used in the characterization of lactoferrin (lf) from colostral whey using anti-lf antibody immunoaffinity chromatography. It was used in the isolation of lactoferrin from bovine colostrum using ultrafiltration coupled with strong cation exchange chromatography.
Azioni biochim/fisiol
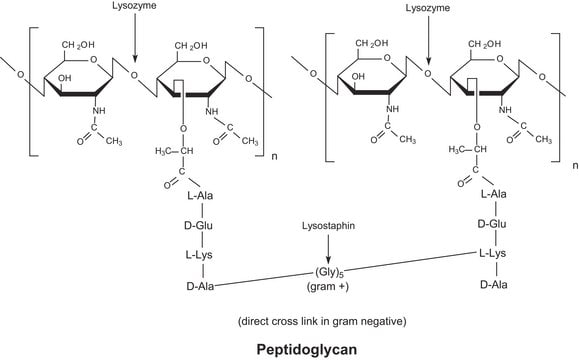
Lactoferrin is an iron binding protein. It is structurally similar to transferrin, the plasma iron transport protein; but lactoferrin has a much higher affinity for iron (250 fold). It is very abundant in colostrum and small amounts can also be found in tears, saliva, mucous secretions and in the secondary granules of neutrophils. It is made by mucosal epithelium and neutrophils and is released by these cells in response to inflammatory stimuli. Bacterial growth is inhibited by its ability to sequester iron and also permeabilize bacterial cell walls by binding to lipopolysaccharides through its N-terminus. Lactoferrin can inhibit viral infection by binding tightly to the viral envelope protein. This prevents cell-virus fusion by blocking the binding domain. Lactoferrin appears to activate host defense systems in part by stimulating the release of interleukin-8, a neutrophil activator. It may also be involved in antibody and interleukin synthesis, lymphocyte proliferation and complement activation.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Andrew S Cooke et al.
PeerJ, 8, e8631-e8631 (2020-05-06)
Promoting and maintaining health is critical to ruminant welfare and productivity. Within human medicine, faecal lactoferrin is quantified for routine assessment of various gastrointestinal illnesses avoiding the need for blood sampling. This approach might also be adapted and applied for
Serena Belegrinou et al.
Langmuir : the ACS journal of surfaces and colloids, 24(14), 7251-7261 (2008-06-14)
The interaction of the proteins bovine serum albumin (BSA), lysozyme (Lys), lactoferrin (Lf), and fibronectin (Fn) with surfaces of protein-resistant poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) and protein-adsorbing poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) fabricated by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition has been studied with quartz crystal
Structural and functional characteristics of bovine milk protein glycosylation
O Riordan N, et al.
Glycobiology, 24(3), 220-236 (2014)
Isolation of lactoferrin from bovine colostrum by ultrafiltration coupled with strong cation exchange chromatography on a production scale
Lu RR, et al.
Journal of Membrane Science , 297(1-2), 152-161 (2007)
Characterization of Lactoferrin (LF) from Colostral Whey Using Anti-LF Antibody Immunoaffinity Chromatography
Y.-Y. Tu, C.-C. Chen, J-H. Chang and H-M. Chang.
Journal of Food Science, 67, 996-1001 (2002)
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.