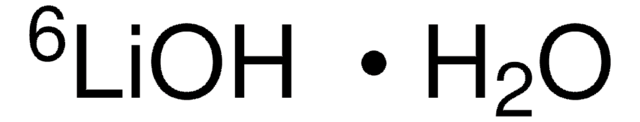13020
Lithium hydroxide monohydrate
purum, ≥98.5%
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Grado
purum
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥98.5%
Stato
crystalline
Impurezze
≤1% Li2CO3
pH
12 (0.4 g/L)
Anioni in tracce
chloride (Cl-): ≤500 mg/kg
sulfate (SO42-): ≤500 mg/kg
Cationi in tracce
Ca: ≤500 mg/kg
Fe: ≤10 mg/kg
K: ≤200 mg/kg
Na: ≤200 mg/kg
Stringa SMILE
[Li+].O.[OH-]
InChI
1S/Li.2H2O/h;2*1H2/q+1;;/p-1
GLXDVVHUTZTUQK-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
8B - Non-combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Ci dispiace, ma al momento non ci sono COA disponibili online per questo prodotto.
Se ti serve aiuto, non esitare a contattarci Servizio Clienti
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.