43963
Moxalactam Supplement
suitable for microbiology
Sinonimo/i:
Listeria MOX Supplement
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Sterilità
sterile
Livello qualitativo
Stato
powder
Durata
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
applicazioni
environmental
food and beverages
microbiology
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Compatibilità
Listeria spp.
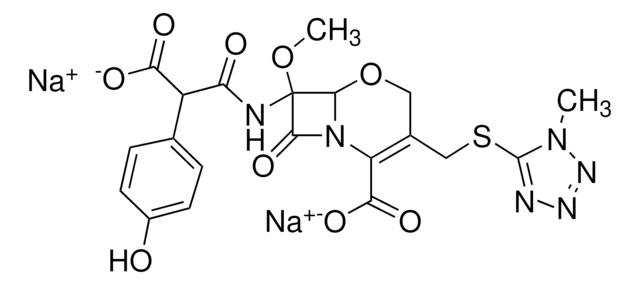
Stringa SMILE
CO[C@]2(NC(=O)C(C(O)=O)c1ccc(O)cc1)[C@H]3OCC(CSc4nnnn4C)=C(N3C2=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C20H20N6O9S/c1-25-19(22-23-24-25)36-8-10-7-35-18-20(34-2,17(33)26(18)13(10)16(31)32)21-14(28)12(15(29)30)9-3-5-11(27)6-4-9/h3-6,12,18,27H,7-8H2,1-2H3,(H,21,28)(H,29,30)(H,31,32)/t12?,18-,20+/m1/s1
JWCSIUVGFCSJCK-CAVRMKNVSA-N
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
Componenti
Moxalactam 20.0 mg
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.