121800-M
Advanced Glycation Endproduct-BSA
AGE-BSA has been reported to induce apoptosis in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells and inhibit nitric oxide synthase activity in proximal tubular epithelial cells.
Sinonimo/i:
AGE-BSA
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Codice UNSPSC:
12352202
NACRES:
NA.25
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
Stato
liquid
Produttore/marchio commerciale
Calbiochem®
Condizioni di stoccaggio
OK to freeze
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
Temperatura di conservazione
−70°C
Descrizione generale
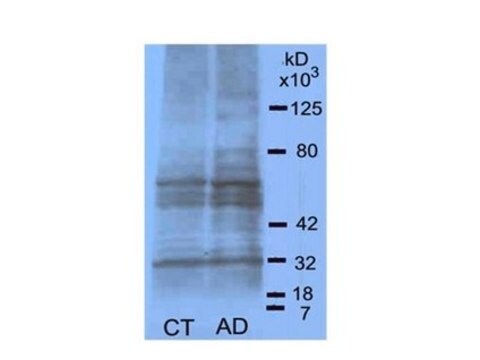
Prepared by reacting BSA with glycoaldehyde under sterile conditions. Glycated-BSA shows a 5,000 - 10,000% increase in fluorescence as compared to normal BSA (confirmed by fluorescence spectrophotometry, excitation/emission 370/440 nm). AGE-BSA has been reported to induce apoptosis in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells and inhibit nitric oxide synthase activity in proximal tubular epithelial cells. Advanced glycation end products and their receptors have been implicated in the pathogenesis of diabetes, induction of proinflammatory cytokines, and stimulation of smooth muscle proliferation, and fibronectin production.
Prepared by reacting bovine serum albumin (BSA) with glycoaldehyde under sterile conditions. Fluorescence of AGE-BSA is confirmed by fluorescence spectrophotometry, excitation/emission = 370/440 nm. Glycated BSA shows a 5000-10,000% increase in fluorescence compared to control BSA. AGE and their receptors have been implicated in the pathogenesis of diabetes, induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and stimulation of smooth muscle proliferation and fibronectin production. AGE-BSA has also been shown to induce apoptosis in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and inhibit nitric oxide synthase activity in proximal tubular epithelial cells of the kidney.
Attenzione
Toxicity: Standard Handling (A)
Stato fisico
In sterile-filtered PBS.
Altre note
Okamoto, T., et al. 2002. Microvasc. Res.63, 186.
Ohgami, N., et al. 2001. J. Biol. Chem.276, 3195.
Wang, R., et al. 2001. J. Nippon Med. Sch.68, 472.
Sakata, N., et al. 2000. J. Atheroscler. Thromb.7, 169.
Verbeke, P., et al. 2000. Biochim. Biophys. Acta1502, 481.
Farboud, B., et al. 1999. Mol. Vis.5, 11.
Huang, J.-S., et al. 1999. Biochem. J.342, 231.
Min, C., et al. 1999. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.46, 197.
Neumann, A., et al. 1999. FEBS Lett.453, 283.
Stitt, A.W., et al. 1999. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.256, 549.
Nazaimoon, W. and Bak, K. 1998. Malays. J. Pathol.20, 83.
Ohgami, N., et al. 2001. J. Biol. Chem.276, 3195.
Wang, R., et al. 2001. J. Nippon Med. Sch.68, 472.
Sakata, N., et al. 2000. J. Atheroscler. Thromb.7, 169.
Verbeke, P., et al. 2000. Biochim. Biophys. Acta1502, 481.
Farboud, B., et al. 1999. Mol. Vis.5, 11.
Huang, J.-S., et al. 1999. Biochem. J.342, 231.
Min, C., et al. 1999. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.46, 197.
Neumann, A., et al. 1999. FEBS Lett.453, 283.
Stitt, A.W., et al. 1999. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.256, 549.
Nazaimoon, W. and Bak, K. 1998. Malays. J. Pathol.20, 83.
Note legali
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 2
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.