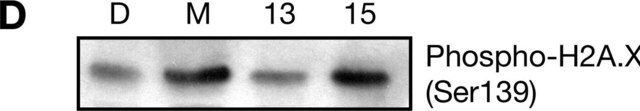
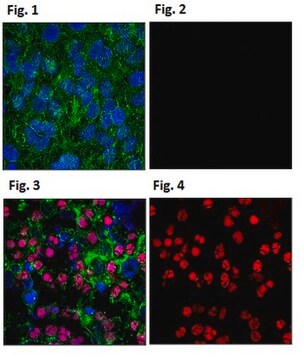
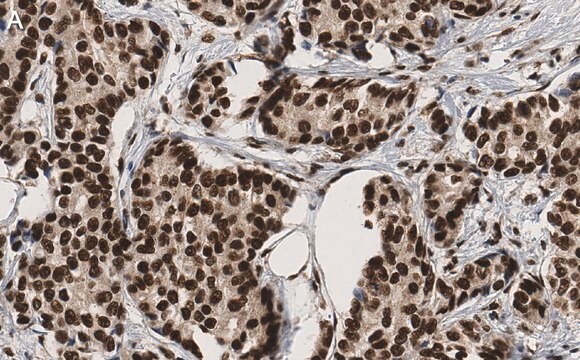
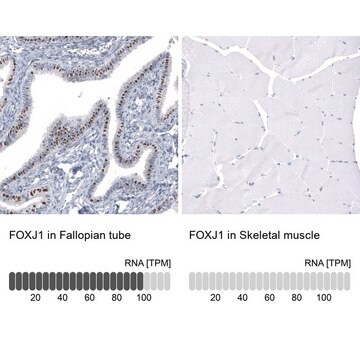
05-726
Anti-53BP1 Antibody, clone BP13
clone BP13, Upstate®, from mouse
Sinonimo/i:
Anti-53BP1, Anti-p202, Anti-p53BP1
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
mouse
Livello qualitativo
Forma dell’anticorpo
purified antibody
Tipo di anticorpo
primary antibodies
Clone
BP13, monoclonal
Reattività contro le specie
human
Produttore/marchio commerciale
Upstate®
tecniche
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
Isotipo
IgG1
N° accesso NCBI
N° accesso UniProt
Condizioni di spedizione
wet ice
modifica post-traduzionali bersaglio
unmodified
Informazioni sul gene
human ... TP53BP1(7158)
Specificità
Immunogeno
Applicazioni
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Transcription Factors
Qualità
Descrizione del bersaglio
Stato fisico
Stoccaggio e stabilità
Note legali
Esclusione di responsabilità
Non trovi il prodotto giusto?
Prova il nostro Motore di ricerca dei prodotti.
Raccomandato
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.