900188
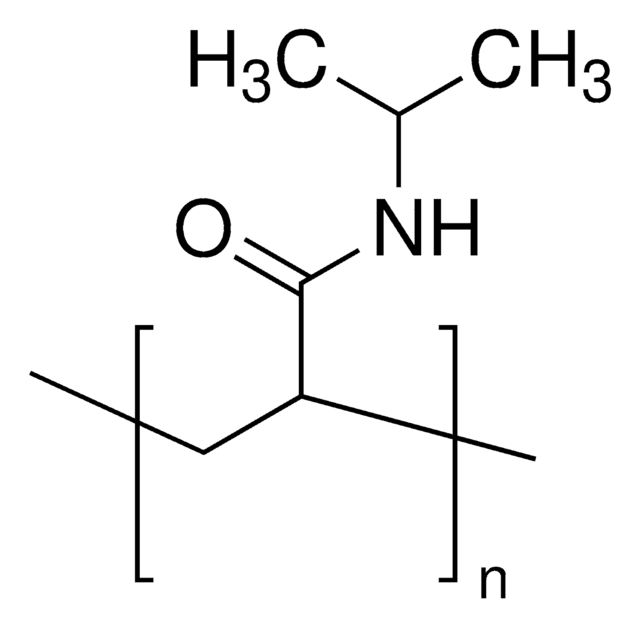
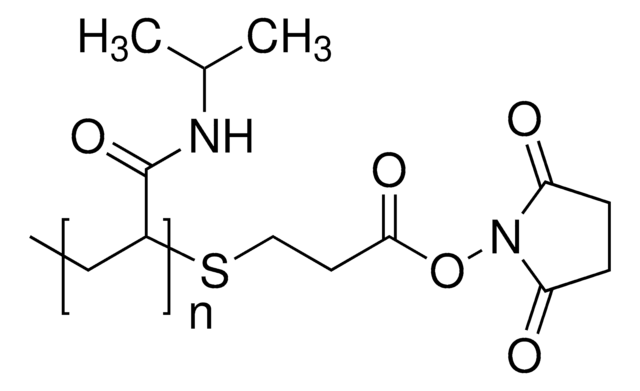
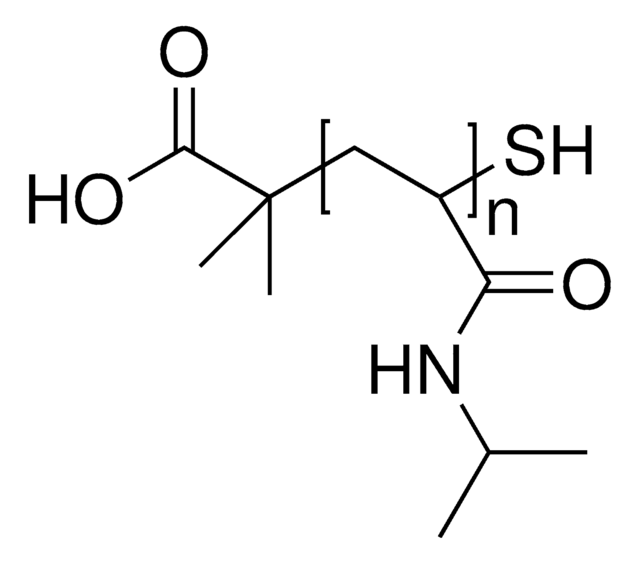
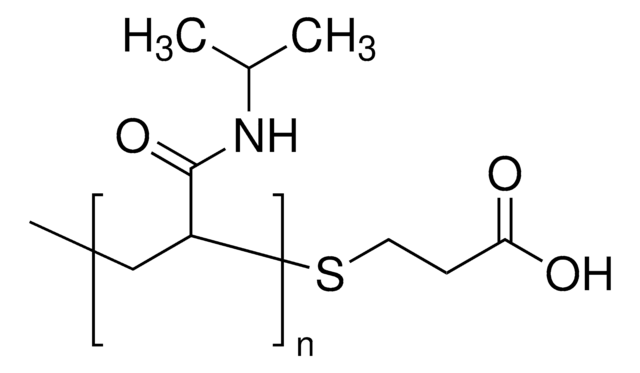
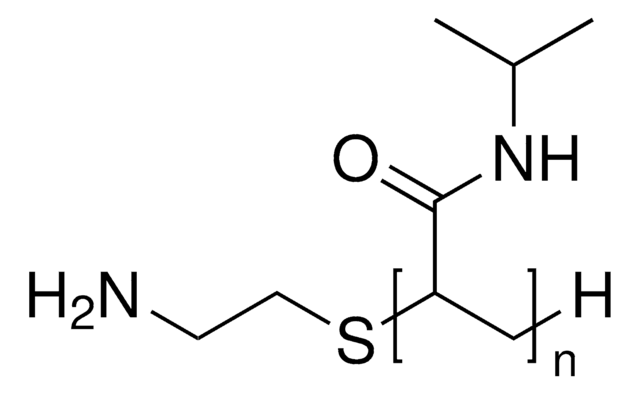
Poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)
NHS ester end functionalized, average Mn 5,000
Sinonimo/i:
PNIPAM, polyNIPAM
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
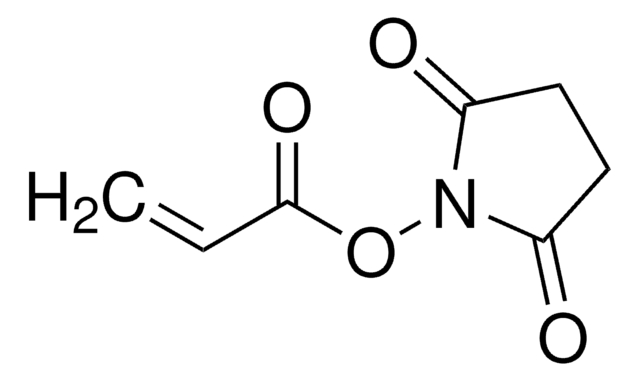
Formula condensata:
C8H10NO4(C6H11NO)nH
Codice UNSPSC:
12162002
NACRES:
NA.23
Prodotti consigliati
Applicazioni
Poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) (PolyNIPAM) is a stimuli-responsive polymer. This product features low polydispersity (PDI), which typically leads to better reproducibility in applications, and a terminal N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) functional group, allowing for rapid conjugation of biomolecules, small molecules, or other polymers. PolyNIPAM has been used in development of a variety of thermosensitive coated micro/nano materials, including thermoresponsive polymeric drug delivery systems.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documenti section.
Se ti serve aiuto, non esitare a contattarci Servizio Clienti
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Aniket S Wadajkar et al.
Acta biomaterialia, 8(8), 2996-3004 (2012-05-09)
New magnetic-based core-shell particles (MBCSPs) were developed to target skin cancer cells while delivering chemotherapeutic drugs in a controlled fashion. MBCSPs consist of a thermo-responsive shell of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-acrylamide-allylamine) and a core of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) embedded with magnetite nanoparticles. To
Chenglin Yi et al.
Journal of colloid and interface science, 380(1), 90-98 (2012-05-29)
Self-assembled polymeric micelles can be used as efficient particulate emulsifiers. To explore the relationship between micellar structure and emulsification performance, pH- and temperature-responsive self-assembled micelles were prepared and used as emulsifiers, based on a novel grafted polymer poly(styrene-alt-maleic acid)-graft-poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)
Manuel Pernia Leal et al.
ACS nano, 6(12), 10535-10545 (2012-11-03)
We report a procedure to grow thermo-responsive polymer shells at the surface of magnetic nanocarriers made of multiple iron oxide superparamagnetic nanoparticles embedded in poly(maleic anhydride-alt-1-ocatadecene) polymer nanobeads. Depending on the comonomers and on their relative composition, tunable phase transition
William S Turner et al.
Journal of biomedical materials research. Part B, Applied biomaterials, 100(8), 2060-2072 (2012-08-14)
The packaging and delivery of cells for cardiac regeneration has been explored using a variety biomaterials and delivery methods, but these studies often ignore one or more important design factors critical for rebuilding cardiac tissue. These include the biomaterial architecture
Yan Xia et al.
Chemical communications (Cambridge, England), 49(25), 2566-2568 (2013-02-21)
Site-specific protein conjugates with RAFT polymers were synthesized using expressed protein ligation. Stable micelles were formed from both linear block copolymer and Y-shaped conjugates.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.