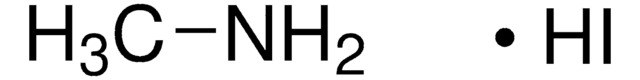806390
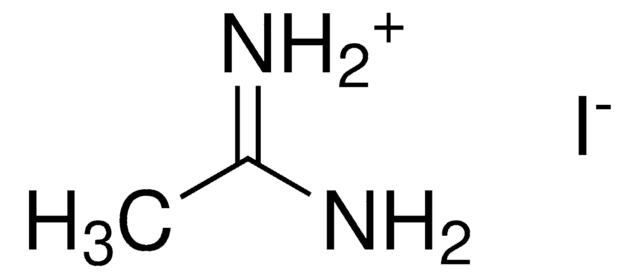
Methylammonium iodide
Sinonimo/i:
Methanamine hydriodide, Greatcell Solar®, Methanaminium iodide, Methylamine hydriodide, Methylamine hydroiodide, Monomethylammonium iodide
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Stato
powder
Livello qualitativo
Caratteristiche più verdi
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Punto di fusione
145 °C
Categoria alternativa più verde
, Enabling
Stringa SMILE
CN.I
InChI
1S/CH5N.HI/c1-2;/h2H2,1H3;1H
LLWRXQXPJMPHLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
Note legali
Avvertenze
Warning
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organi bersaglio
Respiratory system
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
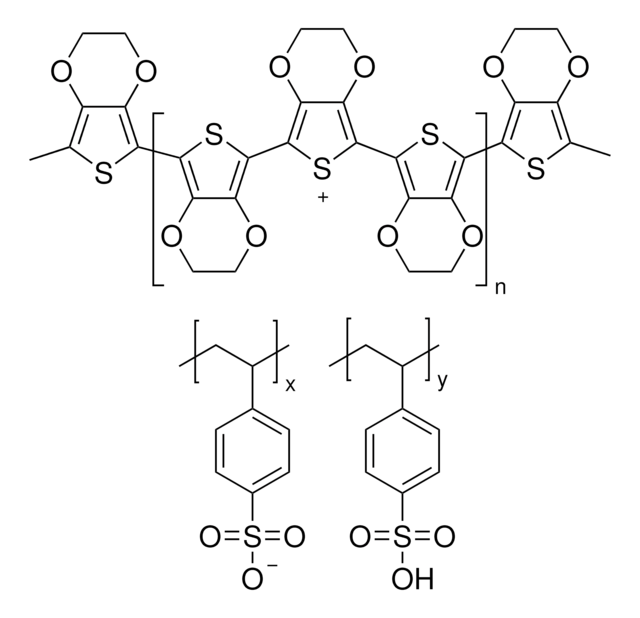
Next generation solar cells have the potential to achieve conversion efficiencies beyond the Shockley-Queisser (S-Q) limit while also significantly lowering production costs.
For several decades, the need for an environmentally sustainable and commercially viable source of energy has driven extensive research aimed at achieving high efficiency power generation systems that can be manufactured at low cost.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.