746762
Lithium hexafluorophosphate solution
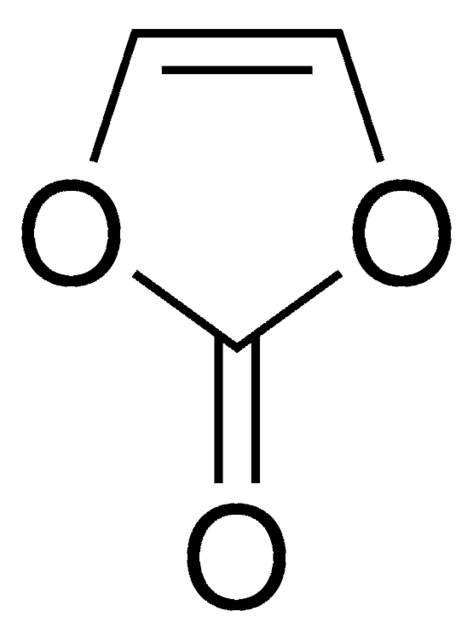
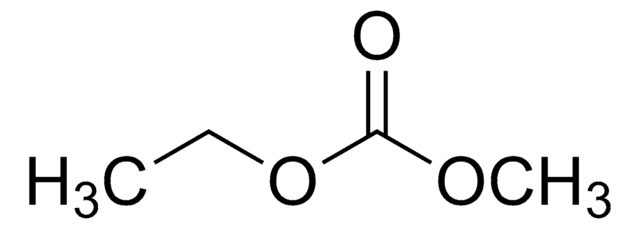
in ethyl methyl carbonate, 1.0 M LiPF6 in EMC, battery grade
Sinonimo/i:
1.0 M LiPF6 EMC, 1.0 M LiPF6 MEC
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Grado
battery grade
Livello qualitativo
Forma fisica
solution
Caratteristiche più verdi
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Concentrazione
(1.0 M LiPF6 in EMC)
Impurezze
<15 ppm H2O
<50 ppm HF
Colore
APHA: <50
P. eboll.
100 °C
Densità
1.12 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Anioni in tracce
chloride (Cl-): ≤1 ppm
sulfate (SO42-): ≤2 ppm
Cationi in tracce
Ca: ≤1 ppm
Fe: ≤1 ppm
K: ≤1 ppm
Na: ≤1 ppm
Pb: ≤1 ppm
applicazioni
battery manufacturing
Categoria alternativa più verde
, Enabling
Stringa SMILE
F[P-](F)(F)(F)(F)F.[Li+]
InChI
1S/F6P.Li/c1-7(2,3,4,5)6;/q-1;+1
AXPLOJNSKRXQPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
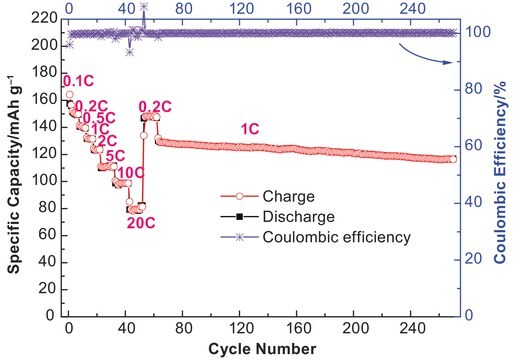
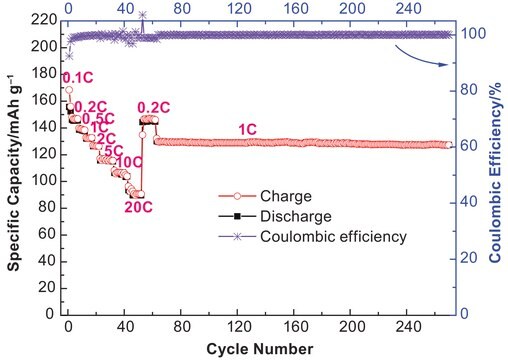
The ready-to-use electrolyte solutions are available in different solvent blends and can support a wide variety of lithium ion battery applications. These solutions are high purity and battery grade thus making them also suitable as standards in LIB research. Customized formulations can be made by inter-mixing the electrolyte solutions or by mixing appropriate of additives.
Altre note
- Do not use with glass equipment
- All work should be done very quickly under dry air to prevent electrolytes from water uptake and solvent vaporization.
Note legali
Prodotti correlati
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT RE 1 Inhalation
Organi bersaglio
Bone,Teeth
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
3 - Flammable liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 2
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
77.0 °F
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
25 °C
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
Dr. Sun reviews the recent advances in solid-state rechargeable batteries and cover the fundamentals of solid electrolytes in solid-state batteries, the theory of ion conduction, and the structures and electrochemical processes of solid-state Li batteries.
Li-ion batteries are currently the focus of numerous research efforts with applications designed to reduce carbon-based emissions and improve energy storage capabilities.
The critical technical challenges associated with the commercialization of electric vehicle batteries include cost, performance, abuse tolerance, and lifespan.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have been widely adopted as the most promising portable energy source in electronic devices because of their high working voltage, high energy density, and good cyclic performance.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.