162957
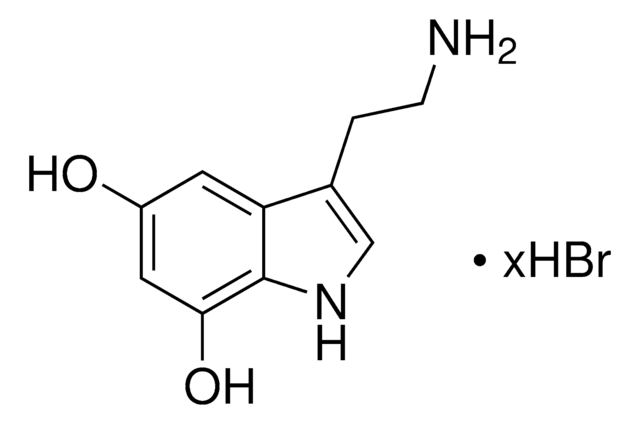
6-Hydroxydopamine hydrobromide
95% (HPLC), powder, neurotoxin
Sinonimo/i:
2,4,5-Trihydroxyphenethylamine hydrobromide, 2,5-Dihydroxytyramine hydrobromide, 2-(2,4,5-Trihydroxyphenyl)ethylamine hydrobromide, 6-OHDA
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Nome del prodotto
6-Hydroxydopamine hydrobromide, 95%
Saggio
95%
Stato
powder
Punto di fusione
216-220 °C (lit.)
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Stringa SMILE
Br.NCCc1cc(O)c(O)cc1O
InChI
1S/C8H11NO3.BrH/c9-2-1-5-3-7(11)8(12)4-6(5)10;/h3-4,10-12H,1-2,9H2;1H
MLACDGUOKDOLGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- to induce Parkinson′s disease (PD) in mouse models to study the effects of tubastatin A (TBA) on nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain and leucine-rich repeat pyrin 3 domain (NLRP3) activation and cell injury in SH-SY5Y cells
- to induce pharmacological ablation of the sympathetic nerves to study the effect of hepatic sympathetic nerve activity (SNA) on hepatic steatosis during diet-induced obesity in mice
- to induce oxidative stress in mesencephalic cells to study its effect on p75NTR signaling in neuronal cells of the ventral mesencephalon
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Avvertenze
Warning
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organi bersaglio
Respiratory system
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.