S9697
Superoxide Dismutase bovine
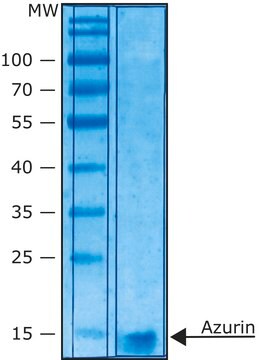
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, lyophilized powder, ≥2500 units/mg protein, ≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
Synonyme(s) :
Superoxide Dismutase 1 bovine, cytocuprein, erythrocuprein, hemocuprein, CU/ZN-SOD, SOD, SOD1, Superoxide: superoxide oxidoreductase
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
bovine
Niveau de qualité
Produit recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Essai
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
Forme
lyophilized powder
Activité spécifique
≥2500 units/mg protein
Conditions de stockage
(Tightly closed)
Technique(s)
inhibition assay: suitable
Couleur
white
pH optimal
7.8 (25 °C)
Plage de pH
7.6-10.5
pl
4.95
Remarque sur la séquence
MATKAVCVLKGDGPVQGTIHFEAKGDTVVVTGSITGLTEGDHGFHVHQFGDNTQGCTSAGPHFNPLSKKHGGPKDEERHVGDLGNVTADKNGVAIVDIVDPLISLSGEYSIIGRTMVVHEKPDDLGRGGNEESTKTGNAGSRLACGVIGIAK
Numéro d'accès UniProt
Température de stockage
−20°C
Description générale
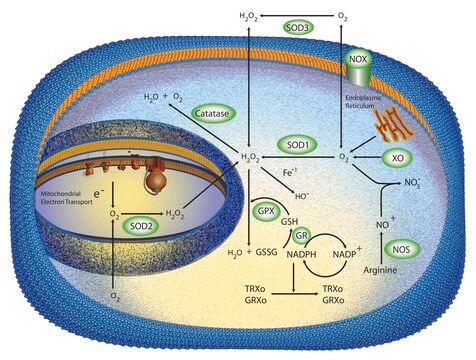
SOD from bovine erythrocytes was the first SOD to be found in mammalian tissues. There are three forms of SOD differentiated by the metal ions in the active site. These are Cu+2/Zn+2, Mn+2, and Fe+2 SOD. In vertebrates, Cu/Zn-SOD is found in the cytoplasm, chloroplast, and may be in extracellular space, while Mn-SOD is found in the mitochondrial matrix space and peroxisome. Fe-SOD is found in the chloroplast of prokaryotes and some higher plants.
Application
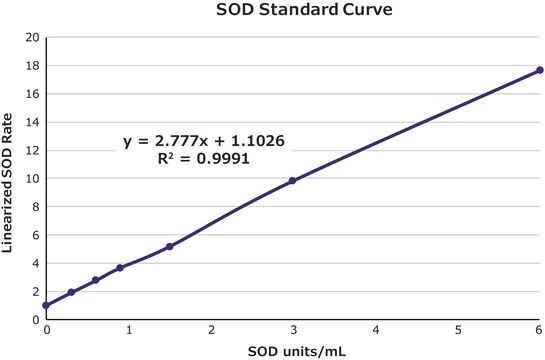
- to construct a calibration curve for the evaluation of superoxide dismutase (SOD) enzyme activities
- in a study to investigate where lipoproteins may affect the L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway
- in a study to investigate the mass spectral evidence for carbonate-anion-radical-induced posttranslational modification of tryptophan to kynurenine in human Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Définition de l'unité
Notes préparatoires
Reconstitution
Remarque sur l'analyse
SOD has no significant absorbance peak at 280 nM because of the absence of tryptophan.
Autres remarques
Anticorps
Produit(s) apparenté(s)
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Resp. Sens. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Oxidative stress is mediated, in part, by reactive oxygen species produced by multiple cellular processes and controlled by cellular antioxidant mechanisms such as enzymatic scavengers or antioxidant modulators. Free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species, cause cellular damage via cellular.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique